Unravelling the relationship between biological diversity and ecosystem functions is a timeless question which dates back to the expeditions of Alexander von Humboldt in the early 1800’. At the base of the marine foodweb, marine prokaryotes are essential for ecosystem functioning. Measuring their biogeography and functional traits therefore merits investigation as alterations in their alpha and beta diversities could lead to changes in the fluxes of oceanic biogeochemical cycles that sustain the life on Earth.
In a new article, published in Nature Communications, the authors used the genetic fingerprint of marine bacteria to predict their metabolic profiles from the ice edge to the equator in the Pacific Ocean. Their research showed that low-cost, high-throughput bacterial marker gene data can be used as a tool for large-scale functional ecology. They tackled five hypotheses and show how biological diversity influences functional diversity, and how these are related to energy production in the ocean. The authors, furthermore, highlight how - can be nicely integrated with the physical and chemical sampling programs during global ocean monitoring campaigns such as GO-SHIP and GEOTRACES.
Increasing our understanding how bacterial diversity impacts the functional diversity of ecosystems has also broader implications. For example, bacterial fingerprints can help us to improve marine ecosystem monitoring programs, especially in coastal zones and estuaries where the input of nitrogen is predicted to increase. Assessing the changes in the bacterial diversity can also help to assess the environmental footprint of aquaculture cages, which are a source of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus and have been shown to deteriorate the water quality and life higher up the food chain.
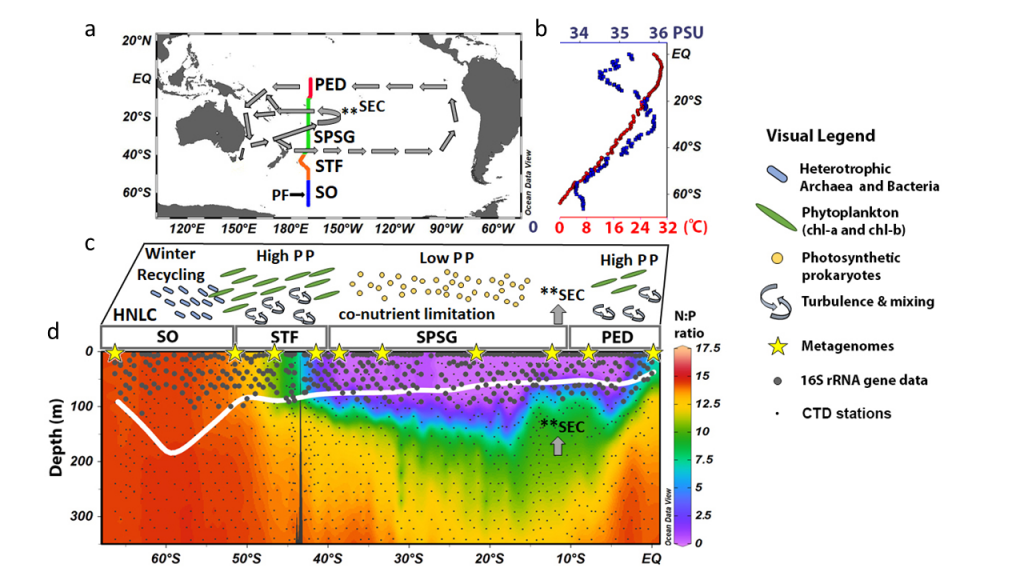
Figure caption: The P15S GO-SHIP line from the ice-edge to the equator along 170o W in the South Pacific Ocean (a). Sea surface temperatures and salinity (b) and a conceptual picture of the functional prokaryotic and microbial-eukaryotic biogeography (c). In winter heterotrophic prokaryotes (blue rods) recycle the organic matter produced in the summer and autumn months in the high nutrient low chlorophyll (HNLC) region of the Southern Ocean (SO). Turbulence and mixing (curved arrows) in the sub-tropical front (STF) results in high primary productivity (PP) driven by phytoplankton rich in chlorophyll-a (green discs). The South Pacific Subtropical Gyre Province (SPSG) is characterized by nutrient co-limitation, low PP, and higher abundances of photosynthetic prokaryotes (yellow circles). The Pacific Equatorial Divergence (PED) is characterized by equatorial upwelling which results in an increase of the N:P ratio in the mixed layer (MLD) relative to the SPSG (d), and results in increased chlorophyll-a concentrations and PP. The MLD is shown as a thick white line. CTD stations (small gray dots), sampling stations for 16S rRNA data (large gray circles) and shotgun metagenome samples (yellow stars) are shown on panel d.
Authors:
Eric J. Raes (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia; Dalhousie University, Canada)
Kristen Karsh (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia)
Swan L. S. Sow (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia; University of Tasmania, Hobart; NIOZ Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, The Netherlands)
Martin Ostrowski (University of Technology Sydney, Australia)
Mark V. Brown (The University of Newcastle, Australia)
Jodie van de Kamp (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia)
Rita M. Franco-Santos (University of Tasmania, Australia)
Levente Bodrossy (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia)
Anya M. Waite (Dalhousie University, Canada)
Read this related general audience article in The Conversation
Want to read more about the P15S line?
Raes, E. J., Bodrossy, L., Van De Kamp, J., Bissett, A., Ostrowski, M., Brown, M. V., ... & Waite, A. M. (2018). Oceanographic boundaries constrain microbial diversity gradients in the South Pacific Ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(35), E8266-E8275.
Raes, E. J., van de Kamp, J., Bodrossy, L., Fong, A. A., Riekenberg, J., Holmes, B. H., ... & Waite, A. M. (2020). N2 fixation and new insights into nitrification from the ice-edge to the equator in the South Pacific Ocean. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 389.
Sow, S. L., Trull, T. W., & Bodrossy, L. (2020). Oceanographic Fronts Shape Phaeocystis Assemblages: A High-Resolution 18S rRNA Gene Survey From the Ice-Edge to the Equator of the South Pacific. Frontiers in microbiology, 11, 1847.