Despite major advances in ocean observing capabilities, characterizing the vertical distribution of materials in the ocean with high spatial resolution remains challenging. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), a technique that relies on measurement of the “time-of-flight” of a backscattered laser pulse to determine the range to a scattering object, could potentially fill this critical gap in our sampling capabilities by providing remote estimates of the vertical distribution of optical properties and suspended particles in the ocean.
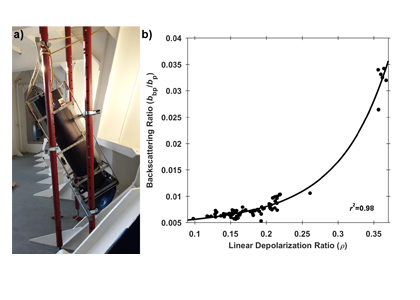
A recent article in Remote Sensing of Environment details the development of a portable shipboard LiDAR and its capabilities for extending high-frequency measurements of scattering particles into the vertical dimension. The authors deployed the experimental system (shown in Figure 1a) during research cruises off the coast of Virginia and during a passenger ferry crossing of the Gulf of Maine (associated with the Gulf of Maine North Atlantic Time Series program-GNATS). Remote measurements of LiDAR signal attenuation corresponded well with simultaneous in situ measurements of water column optical properties and proxies for the concentration of suspended particles. Interestingly, the researchers also observed that the extent to which the return signal was depolarized (also known as the LiDAR depolarization ratio) may provide information regarding the composition of particles within the scattering volume. This is evidenced by the strong relationship between the depolarization ratio and the backscattering ratio, an indicator of the bulk composition (mineral vs. organic) of the particles within a scattering medium (Figure 1b).
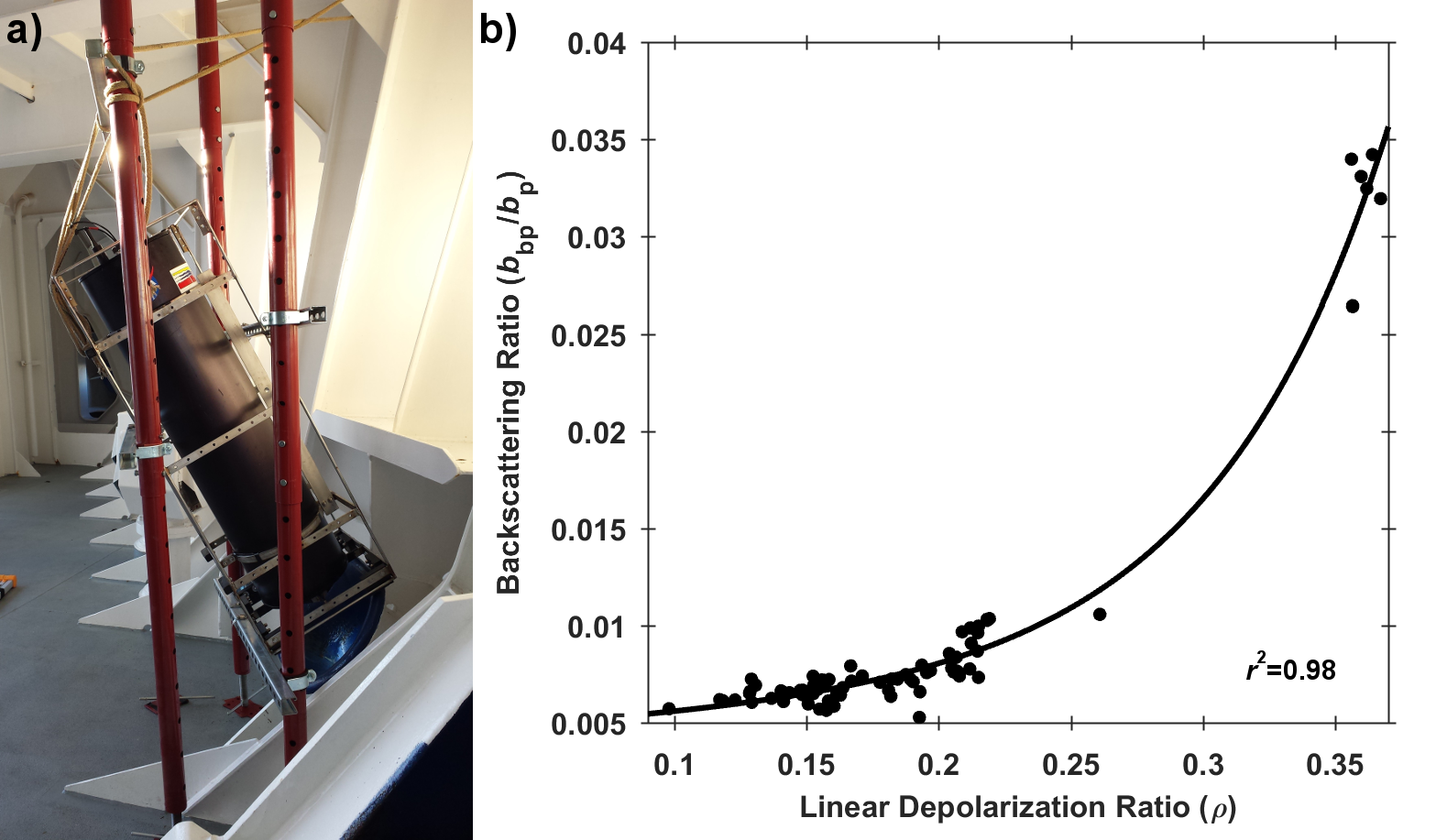
Figure 1. a) LiDAR system deployed to look through a chock at the bow of the M/V Nova Star. b) Relationship between the LiDAR linear depolarization ratio (ρ) and coincident measurements of the particulate backscattering ratio (bbp/bp). The black line represents a least-squares exponential fit to the data.
As LiDAR technology becomes increasingly rugged, compact, and inexpensive, the regular deployment of oceanographic LiDAR on a variety of sampling platforms will become an increasingly practical method for characterizing the vertical and horizontal distribution of particles in the ocean. This has the potential to greatly improve our ability to investigate the role of particles in physical and biogeochemical oceanographic processes, especially when sampling constraints limit observations to the surface ocean.
Authors:
Brian L. Collister (Old Dominion University)
Richard C. Zimmerman (Old Dominion University)
Charles I. Sukenik (Old Dominion University
Victoria J. Hill (Old Dominion University)
William M. Balch (Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences)