The ocean’s biological carbon pump (BCP) is a collection of processes that transport organic carbon from the surface to the deep ocean where the carbon is sequestered for decades to millennia. Variations in the strength of the BCP can substantially change atmospheric CO2 levels and affect the global climate. It is important to accurately estimate this carbon flux, but direct measurement is difficult so this remains a challenge.
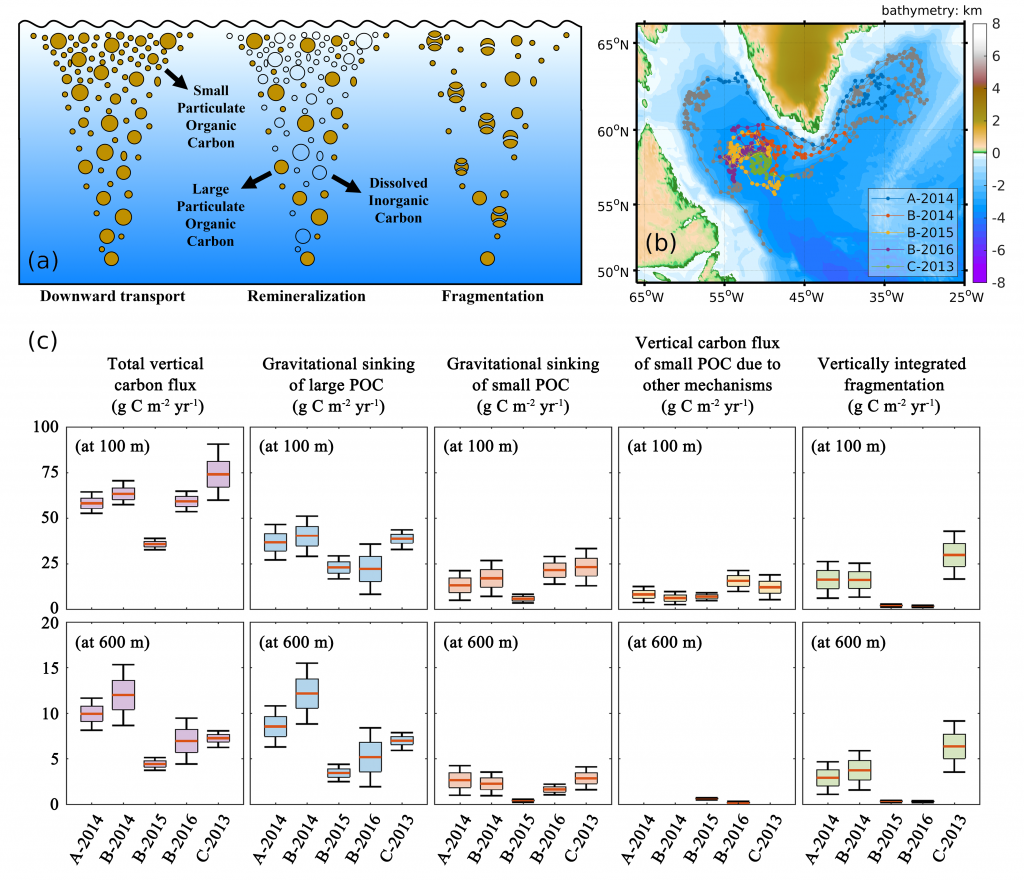
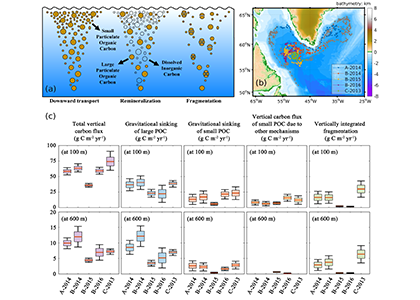
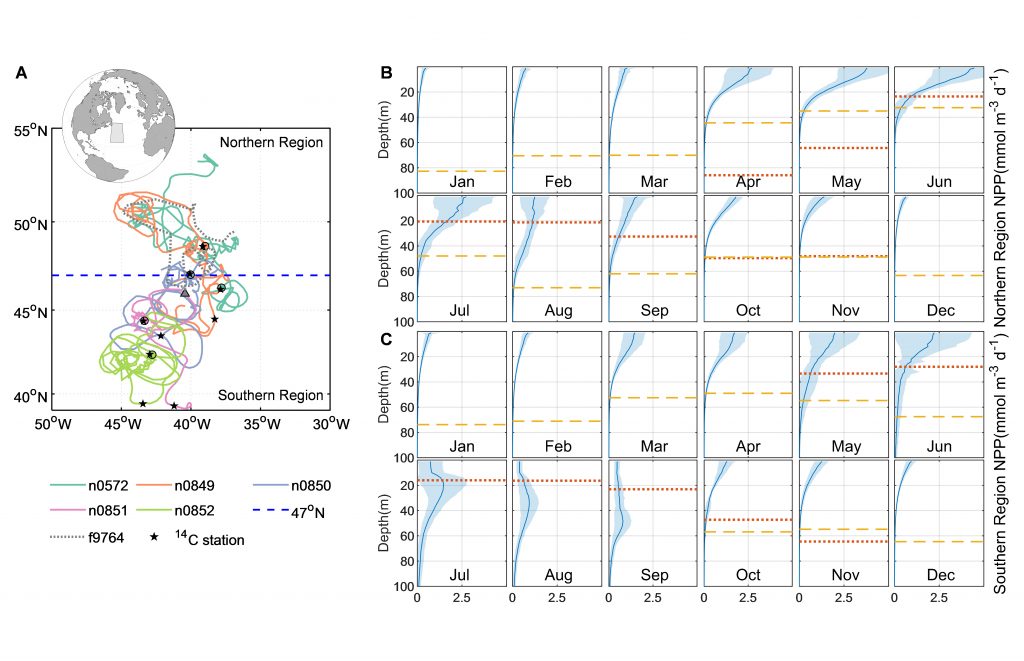
Figure 1. (a) A schematic illustrating the downward transport of small and large POC into the deep ocean and the subsequent remineralization and fragmentation which breaks large POC into small POC. (b) Trajectories of BGC-Argo float segments. (c) Relative contributions to the annually averaged vertical carbon flux show the dominant role of gravitational sinking flux of large POC as well as the significant contributions from small POC at 100 m due to different mechanisms and at 600 m due to fragmentation.
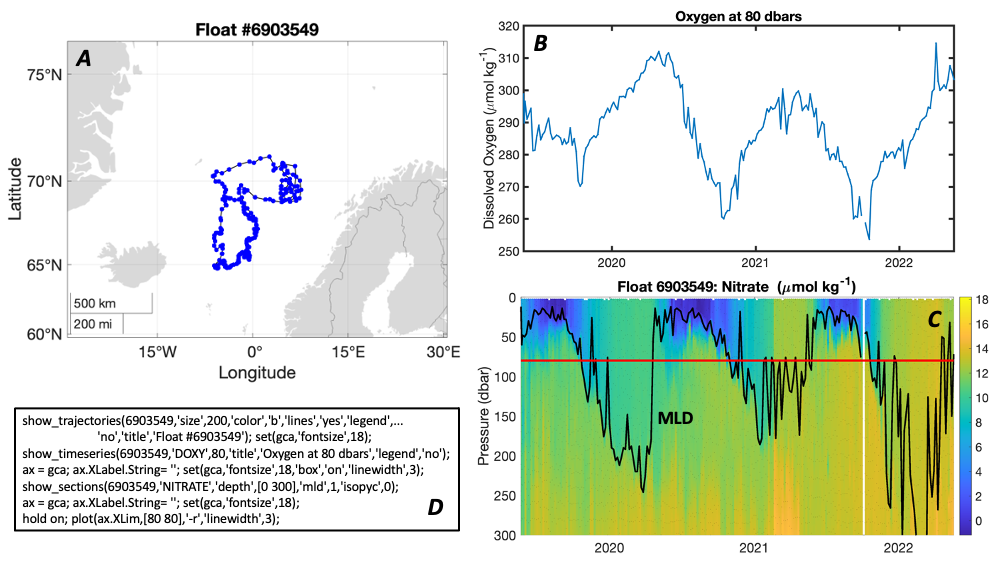
A recent paper published in Limnology and Oceanography performed a novel mass budget analysis using observations of dissolved oxygen and particulate organic carbon (POC) from BGC-Argo floats in the subpolar North Atlantic. The authors assessed relative importance of different mechanisms contributing to the BCP and related processes, the sinking velocity and remineralization rate of different particle size classes as well as the rate of fragmentation which breaks large particles into smaller ones. Results suggest that on annual timescales, the gravitational settling of large POC is the dominant mechanism. Small POC supplements the vertical carbon flux at 100 m significantly, through various mechanisms, and contributes to carbon sequestration below 600 m due to fragmentation of large POC. In addition, sensitivity experiments highlight the importance of considering remineralization and fragmentation when estimating the vertical carbon flux of small POC.
This novel method provides additional independent constraints on current estimates and improves our mechanistic understanding of the BCP. In addition, it demonstrates the great potential of BGC-Argo float data for studying the biological carbon pump.
Authors:
Bin Wang (Dalhousie University)
Katja Fennel (Dalhousie University)