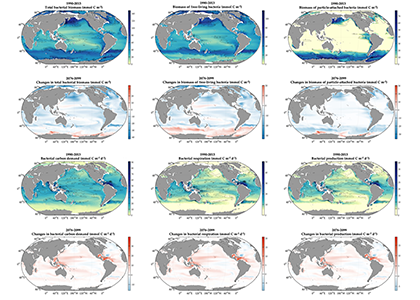
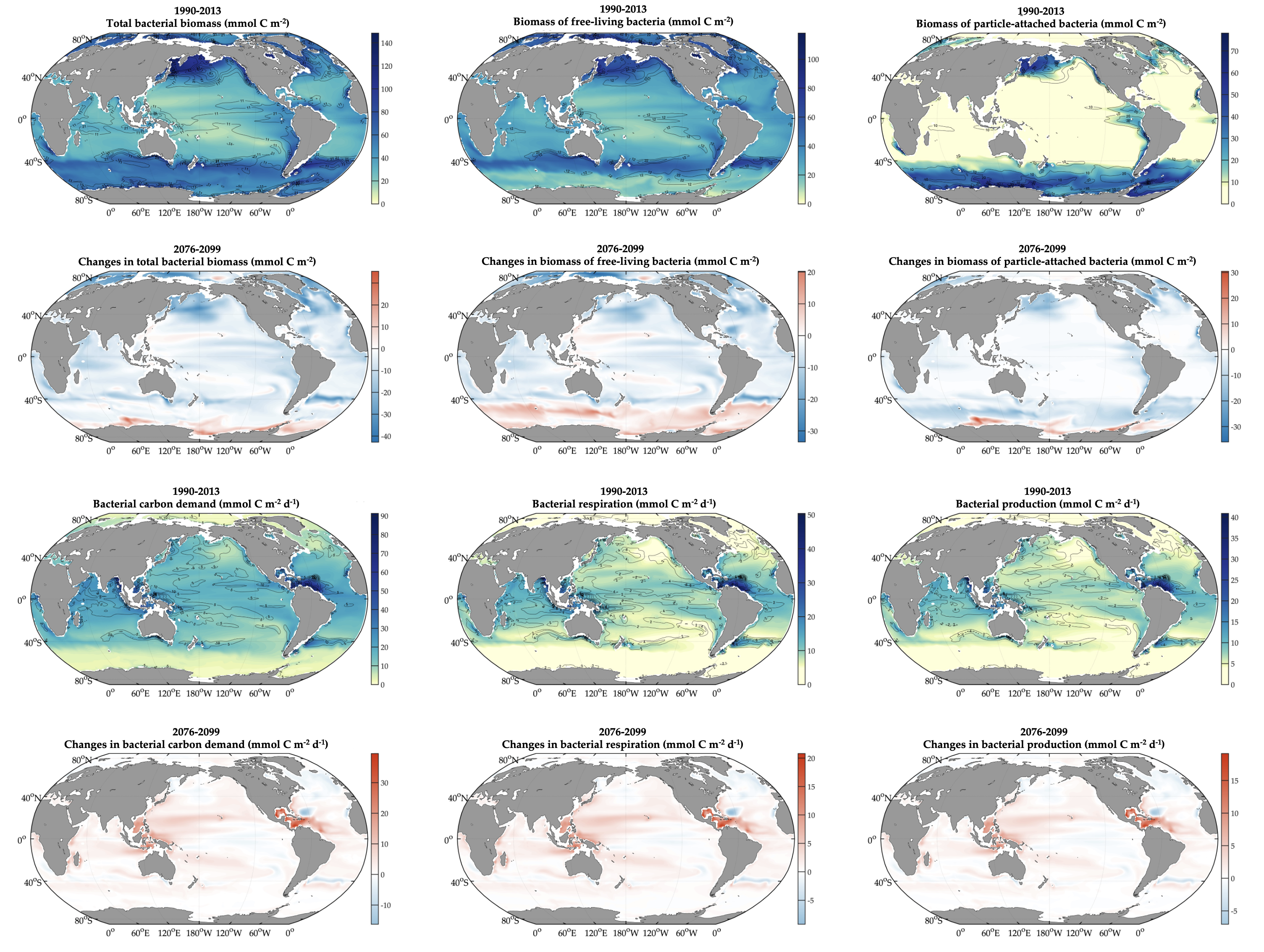
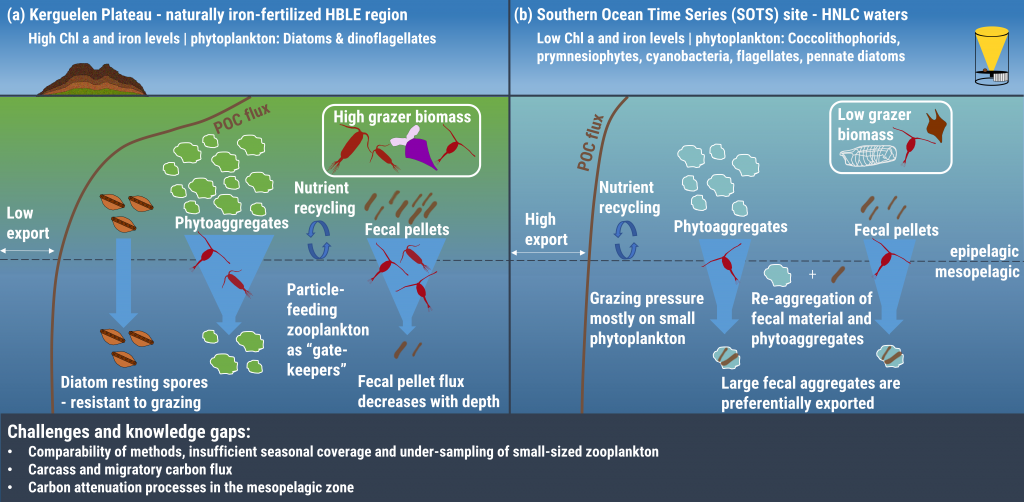
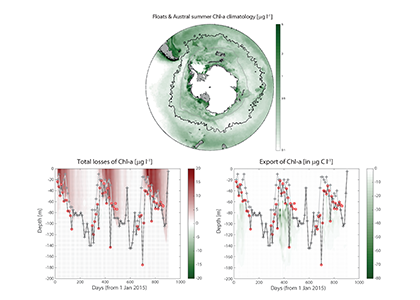
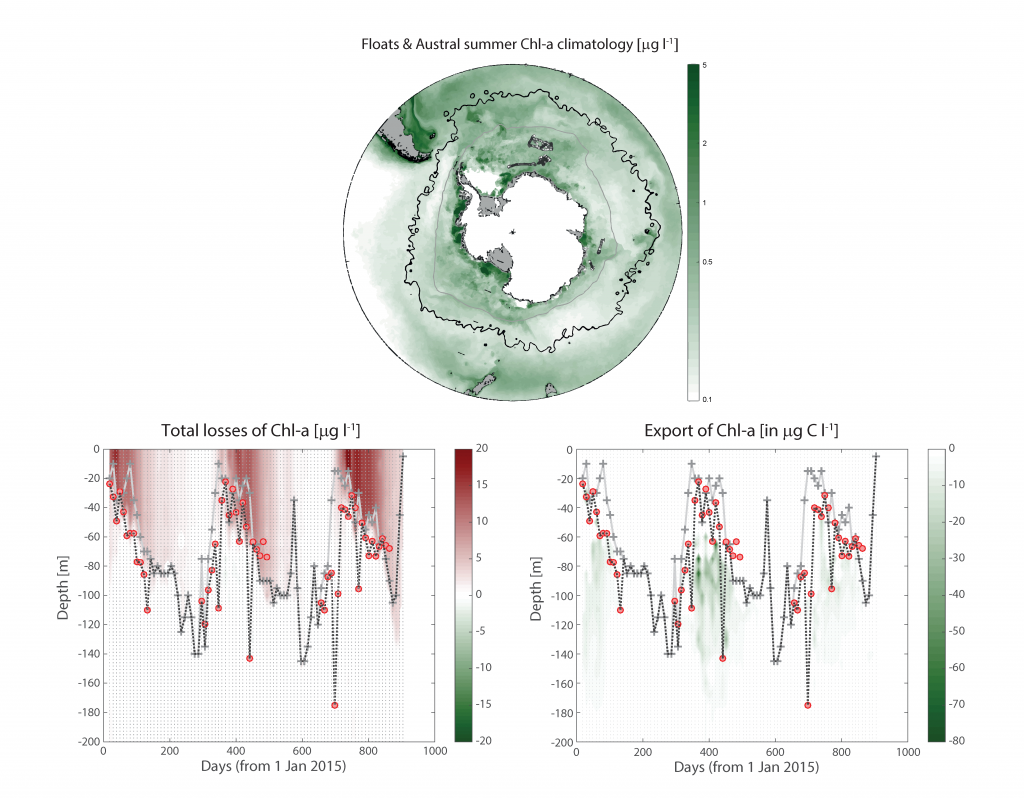
The ocean is the most important sink of anthropogenic emissions and is being considered as a medium to manipulate to draw down even more. Essential in the ocean’s role as a natural carbon-sponge is the net production of organic matter by phytoplankton, some of which sinks and is stored for 100s-1000s of years. Successfully simulating this biological carbon pump is essential for projecting any climate scenario, but it appears that massive uncertainties in the way zooplankton consume phytoplankton are compromising predictions of future climate and our assessment of some strategies to deliberately engineer it.
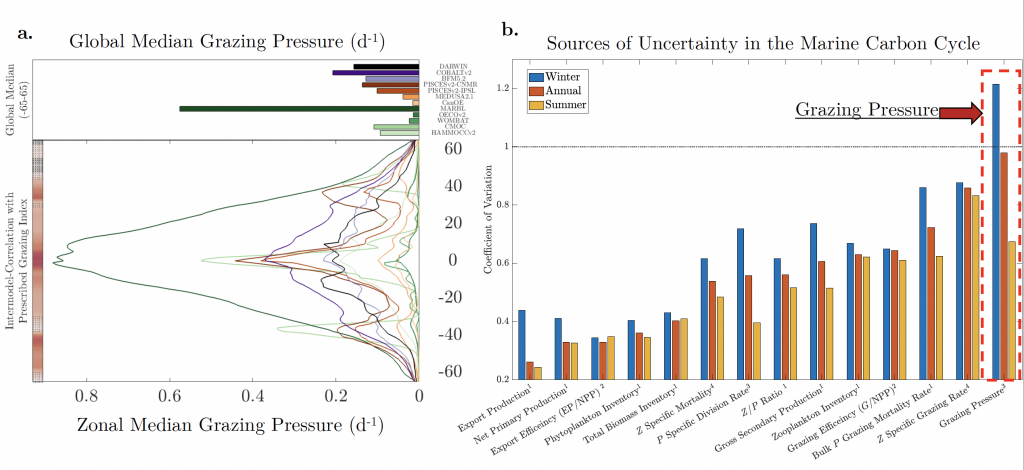
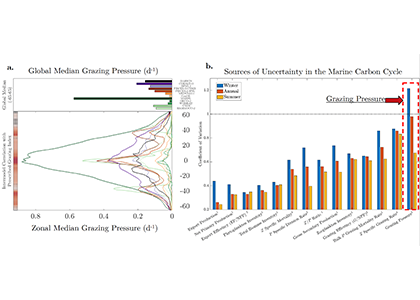
Figure caption. Grazing pressure is largest source of uncertainty for marine carbon cycling in CMIP6 models a) The global and zonal median winter grazing pressure is shown for all models. b) the coefficient of variation across models (std/mean) is largest for grazing pressure compared 14 major terms in the marine carbon cycle.
A new publication in Communications Earth and Environment explains how our poor understanding of zooplankton biases our best projections of marine carbon sequestration. We compared 11 IPCC climate models and found zooplankton grazing is largest source uncertainty in marine carbon cycling. This uncertainty is over three times larger than that of net primary production and is driven by large differences in different models assumptions about the rate at which zooplankton can consume phytoplankton. Yet, very small changes in zooplankton grazing dynamics (roughly only 5% of the full range used across IPCC models) can increase carbon sequestrations by 2 PgC/yr, which is double the maximum theoretical potential of Southern Ocean Iron Fertilization! Moving forward, to move beyond merely treating zooplankton as a closure term, modelers must look towards novel observational constraints on grazing pressure.
Authors
Tyler Rohr, Anthony J. Richardson, Andrew Lenton, Matthew A. Chamberlain, and Elizabeth H. Shadwick
See also the Conversation article