The California Current System is a highly productive coastal upwelling region that supports commercial fisheries valued at $6 billion/year. These fisheries are supported by upwelled waters, which are rich in nutrients and serve as a natural fertilizer for phytoplankton. Due to remineralization of organic matter at depth, these upwelled waters also contain large amounts of dissolved inorganic carbon, causing local conditions to be more acidic than the open ocean. This natural acidity, compounded by the dissolution of anthropogenic CO2 into coastal waters, creates corrosive conditions for shell-forming organisms, including commercial fishery species.
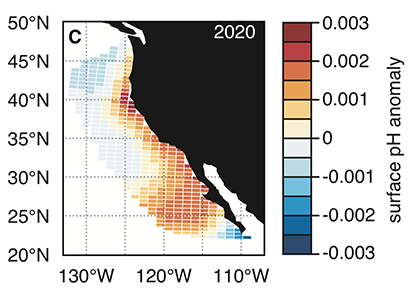
A recent study in Nature Communications showcases the potential for climate models to skillfully predict variations in surface pH—thus ocean acidification—in the California Current System. The authors evaluate retrospective predictions of ocean acidity made by a global Earth System Model set up similarly to a weather forecasting system. The forecasting system can already predict variations in observed surface pH fourteen months in advance, but has the potential to predict surface pH up to five years in advance with better initializations of dissolved inorganic carbon (Figure 1). Skillful predictions are mostly driven by the model’s initialization and subsequent transport of dissolved inorganic carbon throughout the North Pacific basin.
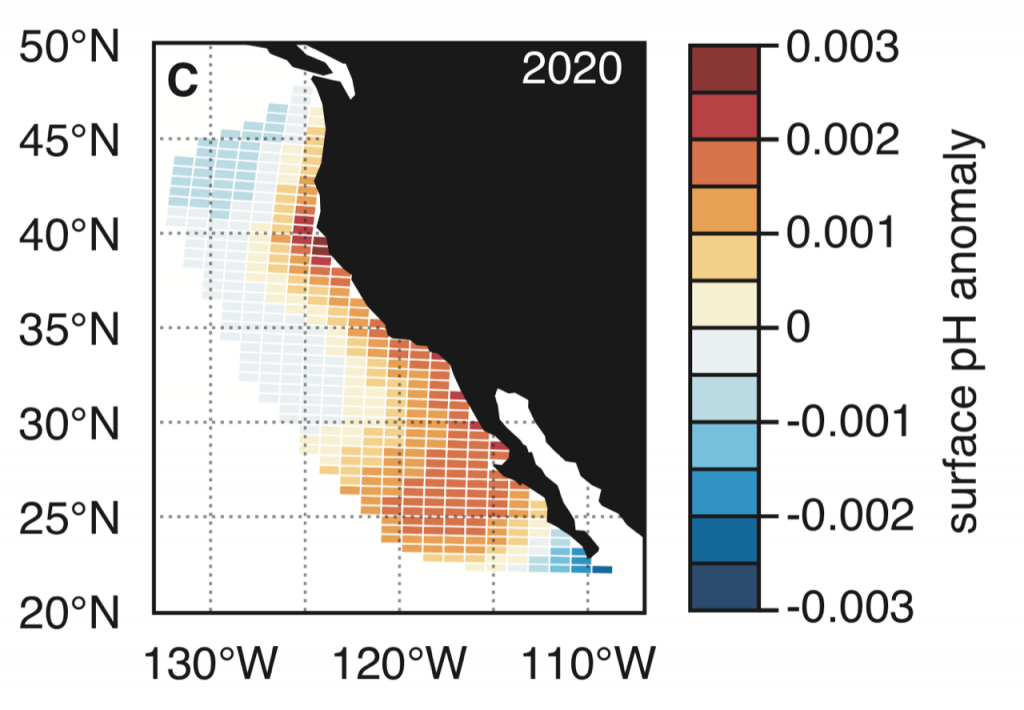
Figure 1. Forecast of annual surface pH anomalies in the California Current Large Marine Ecosystem for 2020. Red colors denote anomalously basic conditions for the given location and blue colors indicate anomalously acidic conditions.
These results demonstrate, for the first time, the feasibility of using climate models to make multiyear predictions of surface pH in the California Current. Output from this global prediction system could serve as boundary conditions for high-resolution models of the California Current to improve prediction time scale and ultimately help inform management decisions for vulnerable and valuable shellfisheries.
Authors:
Riley X. Brady (University of Colorado Boulder)
Nicole S. Lovenduski (University of Colorado Boulder)
Stephen G. Yeager (National Center for Atmospheric Research)
Matthew C. Long (National Center for Atmospheric Research)
Keith Lindsay (National Center for Atmospheric Research)