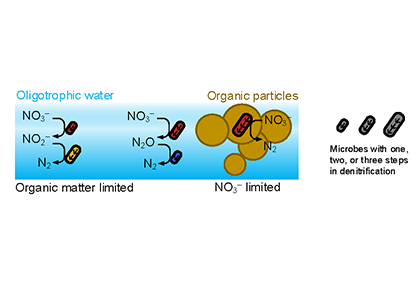
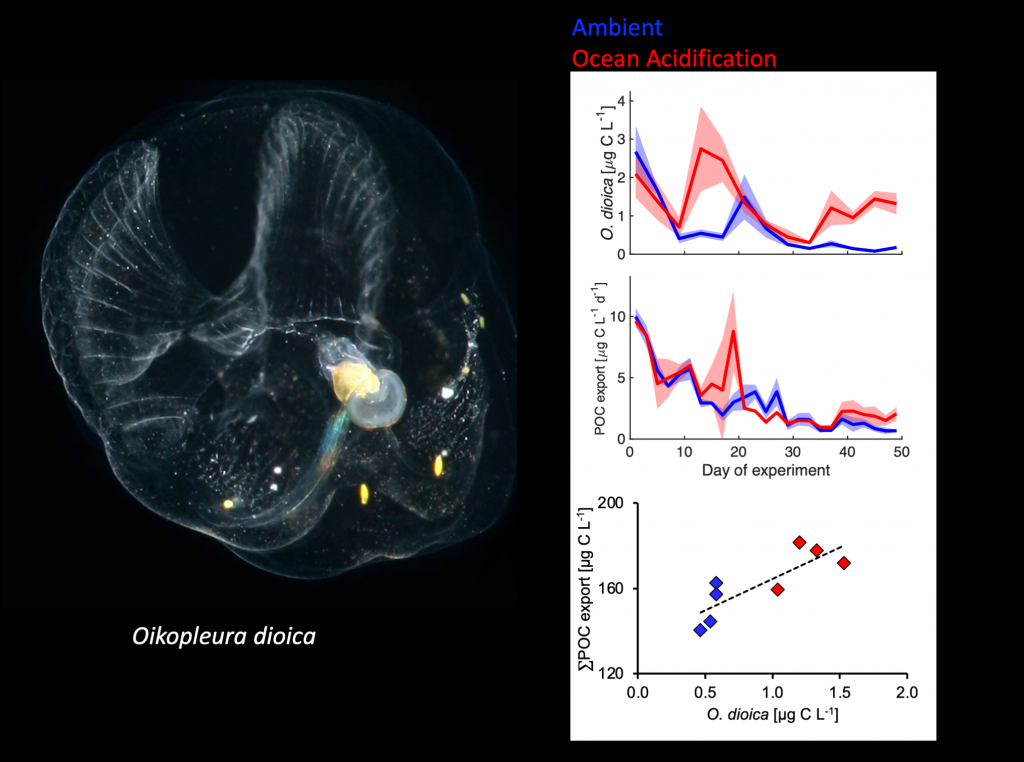
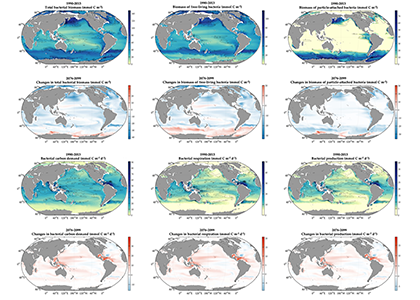
Denitrification is a crucial multi-step process for ecosystem productivity and sustainability because some of its steps can result in the loss of the essential nutrient nitrogen or the production of greenhouse gas nitrous oxide. We do not understand why microbial functional groups conducting different steps of denitrification can coexist in the ocean and why certain groups are more abundant than others.
In a recent study published in PNAS, we uncover ecological mechanisms that govern the coexistence of these microbes. For the microbial groups utilizing different nitrogen substrates, the “stronger” groups rely on the “weaker” groups to feed them nitrogen (with respect to the organic substrates that they compete for), enabling them to coexist. For the groups competing for the same nitrogen substrates, microbes that invest more to build longer denitrification steps win the competition when nitrogen is limiting, but lose the game when nitrogen is repleted and organic carbon is limiting. The spatial and temporal variability of nutrients in the ocean allows these microbes to be observed in the same water mass.
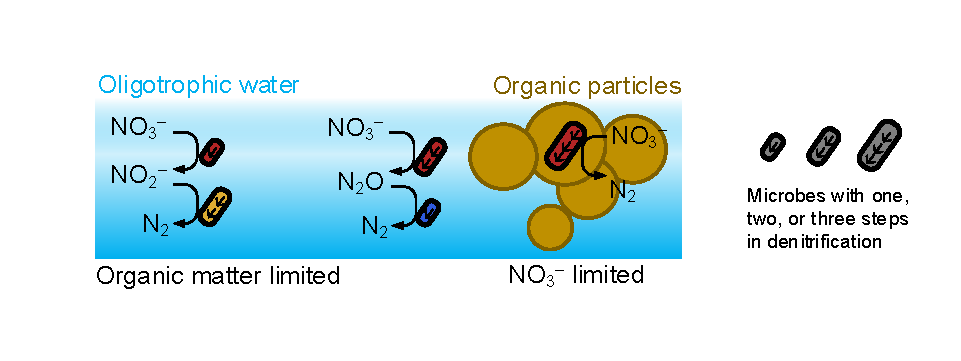
Figure caption: Temporal and spatial heterogeneity in nutrients promotes the coexistence of functionally diverse denitrifiers in the ocean.
These hypothesized coexistence patterns help us predict where and when nitrogen loss and nitrous oxide production may occur. As human activities continue to alter marine nutrient balances, these predictions help us better anticipate ocean responses and design better strategies for mitigating negative anthropogenic impacts on the ocean.
Authors
Xin Sun (Carnegie Institution for Science) @xinsun-putiger.bsky.social
Emily Zakem (Carnegie Institution for Science) @carnegiescience.bsky.social