How much carbon has been buried in the depths of our ancient oceans, and how did it shape our planet’s climate? Unraveling this enigma has long eluded researchers, but a recent groundbreaking “bottom-up” study unveils the surprising history of organic carbon burial in marine sediments during the Neogene period.
Departing from conventional methods, this study presents an innovative approach to calculating organic carbon burial rates independently. Drawing from data collected from 81 globally distributed sites, the research covers the Neogene era (approximately 23 to 3 million years ago). The results reveal unprecedented spatiotemporal variability in organic carbon burial, challenging previous estimates. Notably, high burial rates were found during the early Miocene and Pliocene, contrasting with a significant decline during the mid-Miocene, marked by the lowest ratio of organic-to-carbonate burial rates. This finding disputes earlier interpretations of enriched carbonate 13C values during the mid-Miocene (so called “Monterey Period” or “Monterey Excursion”) as indicative of massive organic carbon burial.
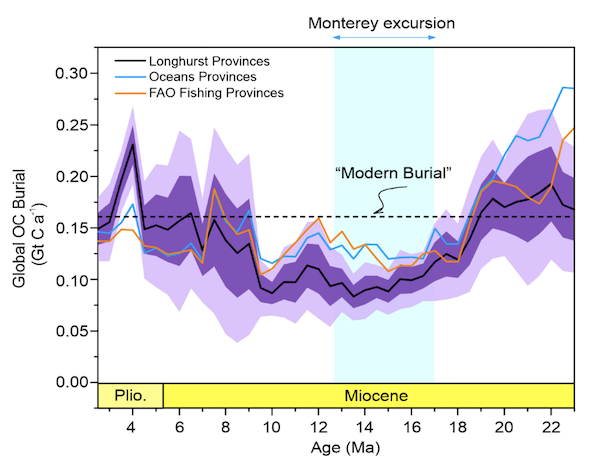
Figure Caption: Neogene organic carbon (OC) burial in the global ocean. Burial rates calculated using different definitions of provinces, including three approaches: Longhurst (black curve with uncertainty envelope,± 1σ in purple and ± 2σ in pale lilac), Oceans (blue curve), and FAO Fishing (orange curve).
Understanding the complex carbon burial dynamics of ancient oceans holds profound implications for comprehending our planet’s climate evolution. The suppressed organic carbon burial during the warm mid-Miocene, likely driven by temperature-dependent bacterial degradation, suggests the organic carbon cycle acted as a positive feedback mechanism during past global warming events. These findings emphasize the vital role of ocean carbon sequestration, providing stark evidence for policymakers, funding agencies, citizens, and educators to acknowledge its significance in combating modern climate challenges.
Authors
Ziye Li (University of Bremen)
Yi Ge Zhang (Texas A&M University)
Mark Torres (Rice University)
Ben Mills (University of Leeds)
Twitter: @chemclimatology
Backstory
Dr. Zhang, a shipboard organic geochemist during International Ocean Discovery Program Expedition 363, embarked on the legendary drilling ship JOIDES Resolution. While on the journey, Yige spent hours and hours daily crushing samples to measure organic carbon until his palm grew calluses, but the TOC% numbers did not really change. Fueled by sheer determination, Yige’s former student Ziye Li and himself delved into 50 years of IODP data archives to uncover global trends, and with the help of carbon cycle modelers Mark Torres and Ben Mills, leading to the discovery of the history of organic carbon burial.