Many scientists have long hypothesized that the ocean around Antarctica was responsible for changing CO2 levels during ice ages, but lacked definitive evidence. A new study in Nature provides the most direct evidence of this process to date and provides crucial evidence of the mechanisms—including changing sea ice cover and bipolar seesaw (warming in the Southern Hemisphere during cooling in the Northern Hemisphere) events—that controlled CO2 and climate during the ice ages.
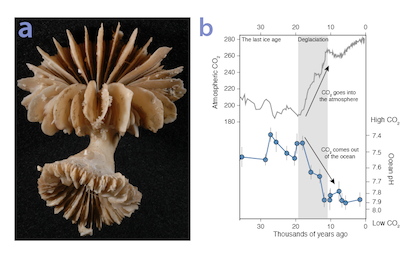
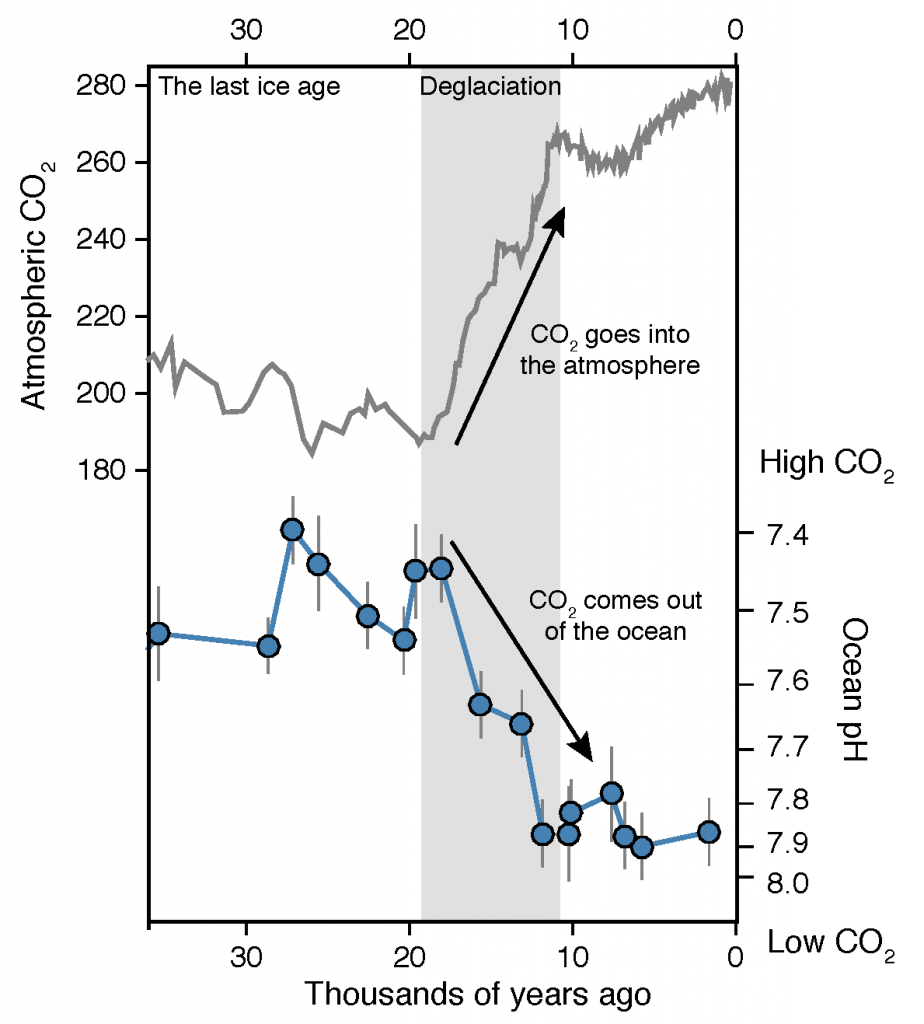
Using samples of fossil deep-sea corals collected from 1000 m in the Drake Passage (Figure 1a), the authors were able to reconstruct the CO2 content of the deep ocean. They found that the deep ocean CO2 record was the “mirror image” of CO2 in the atmosphere (Figure 1b), with the ocean storing CO2 during an ice age and releasing it back to the atmosphere during deglaciation. CO2 rise during the last ice age occurred in a series of steps and jumps associated with intervals of rapid climate change.

As well as helping scientists better understand the ice ages, the new findings also provide context to current CO2 rise and climate change. Although the CO2 rise that helped end the last ice age was dramatic in geological terms, CO2 rise due to human activity over the last 100 years is even larger and about 100 times faster. CO2 rise at the end of the ice age helped drive major melting of ice sheets resulting in sea level rise of >100 meters. These results bolster the idea that if we want to prevent dangerous levels of global warming and sea level rise in the future, we need to reduce CO2 emissions as quickly as possible
Authors:
J. W. B. Rae (University of St Andrews, UK)
A. Burke (University of St Andrews, UK)
L. F. Robinson (University of Bristol, UK)
J. F. Adkins (California Institute of Technology)
T. Chen (University of Bristol, UK, Nanjing University, China)
C. Cole (University of St Andrews, UK)
R. Greenop (University of St Andrews, UK)
T. Li (University of Bristol, UK, Nanjing University, China)
E. F. M. Littley (University of St Andrews, UK)
D. C. Nita (University of St Andrews, UK, Babes-Bolyai University, Romania)
J. A. Stewart (University of St Andrews, UK, University of Bristol, UK)
B. J. Taylor (University of St Andrews, UK)