There are vast unknowns about the future oceans, from what species or habitats may be most under threat to the continuity of earth system processes that maintain global climate. Modeling can be used to predict future states and explore the impacts of climate change, but several key uncertainties such as carbon-climate feedbacks hamper our predictive power.
Authors of a recent study in Biogeosciences (Matear and Lenton 2018) used a global earth system model to explore the effects of carbon-climate feedbacks on future ocean acidification. Ocean acidification can have wide-ranging impacts on keystone species from reef-building corals to pteropods, a major food web species in the Southern Ocean. The study included four representative scenarios (from IPCC) comparing concentration pathway simulations to emission pathway simulations (RCP2.6, RCP 4.5, RCP6, RCP8.5) to determine carbon-climate feedbacks. The high emission scenarios (RCP8.5 and RCP6) showed surface water undersaturation a decade or more earlier than expected. Surprisingly, the medium (RCP4.5) scenario carbon-climate feedbacks showed the greatest acidification response, doubling the extent of undersaturation and subsequently halving the area that could sustain coral reefs by 2100. The low emissions scenario also showed significant declines in saturation state.
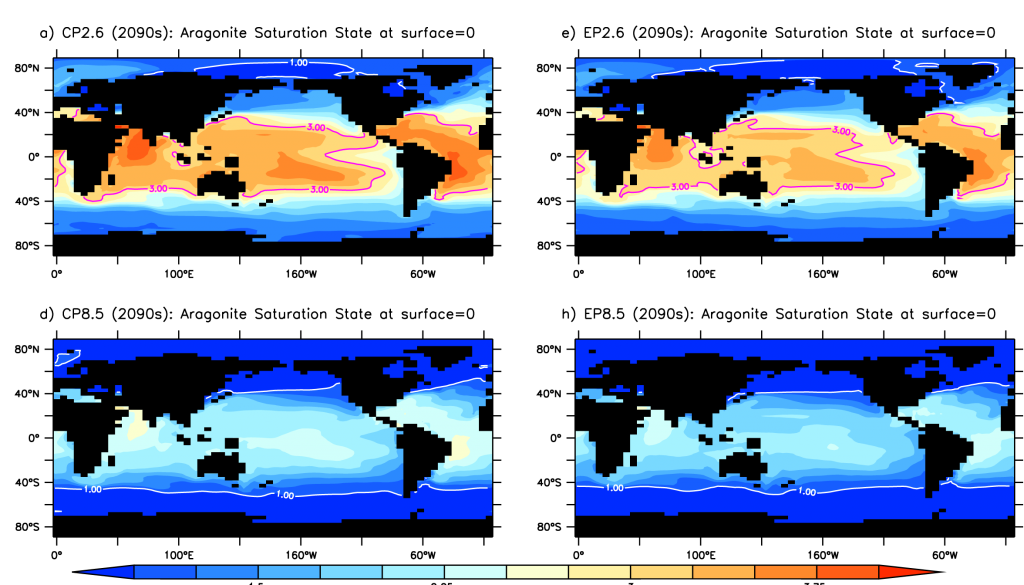
Surface ocean aragonite saturation state for the 2090s for RCP2.6 and RCP 8.5 concentration and emission pathways. The contour line delineates a saturation state of 3 (coral reef threshold), the white line a saturation state of 1, when aragonite becomes unstable and corals dissolve.
The extra atmospheric CO2 from the carbon-climate feedback resulted in accelerated ocean acidification in all emission scenarios. These feedbacks may also affect global warming and deoxygenation. This is particularly important, given that many policymakers are aiming for low emission commitments, but may still be severely underestimating the extent and timing of ocean acidification. There is a great need to improve our ability to predict carbon-climate feedbacks so we do not underestimate projected ocean acidification and its impacts on both sensitive ecosystems and the human communities that rely on them for food, coastal protection and other ecosystem services.
Authors:
Richard Matear (CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Australia)
Andrew Lenton (Antarctic Climate and Ecosystems CRC, Australia)