If you would like to have your recent publications featured on the OCB website please contact ocb_news@whoi.edu. View our guidelines for writing a New OCB Research post.
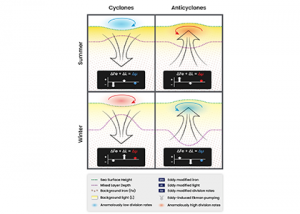
Southern Ocean biological productivity is instrumental in regulating the global carbon cycle. Previous correlative studies associated widespread mesoscale activity with anomalous chlorophyll levels. However, eddies simultaneously modify both the physical and biogeochemical environments via several competing pathways, making it difficult to discern which mechanisms are responsible for the observed biological anomalies within them. Two recently […]
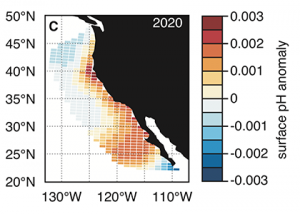
Read MoreThe California Current System is a highly productive coastal upwelling region that supports commercial fisheries valued at $6 billion/year. These fisheries are supported by upwelled waters, which are rich in nutrients and serve as a natural fertilizer for phytoplankton. Due to remineralization of organic matter at depth, these upwelled waters also contain large amounts of […]
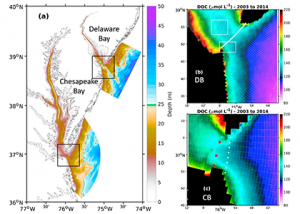
Read MoreDissolved organic carbon (DOC) is a food supplement that supports microorganism growth and plays a major role in the global carbon cycle via the microbial loop, which integrates DOC into the marine food web. DOC from two major estuaries on the US East Coast, Chesapeake (CB) and Delaware Bay (DB), represent major contributors to the […]
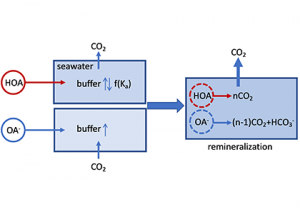
Read MoreThe marine chemistry community has measured organic alkalinity in coastal and estuarine waters for over two decades. While the common perception is that any unaccounted alkalinity should enhance seawater buffer capacity, the effects of organic alkalinity on this buffering capacity, and hence the potential CO2 uptake by coastal and estuarine systems are still not well […]
Read MoreMicroscopic plankton in the surface ocean make planet Earth habitable by generating oxygen and forming the basis of marine food webs, yielding harvestable protein. For over 100 years, oceanographers have tried to ascertain the physical, chemical, and biological processes governing phytoplankton blooms. Zooplankton grazing of phytoplankton is the single largest loss process for primary production, […]
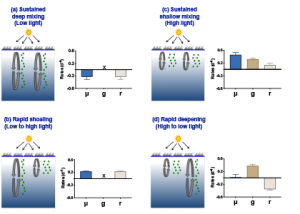
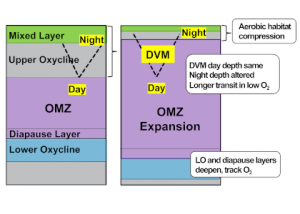
Read MoreGlobal warming increases ocean deoxygenation and expands the oxygen minimum zone (OMZ), which has implications for major zooplankton groups like copepods. Reduced oxygen levels may impact individual copepod species abundance, vertical distribution, and life history strategy, which is likely to perturb intricate oceanic food webs and export processes. In a study recently published in Biogeosciences, […]
Read MoreBlue holes are unique depositional environments that are formed within carbonate platforms. Due to an enclosed geomorphology that restricts water exchange, blue hole ecosystems are typically characterized by steep biogeochemical gradients and distinctive microbial communities. For the past three decades, studies have described vertical gradients in physical, chemical, and biological parameters that typify blue hole […]
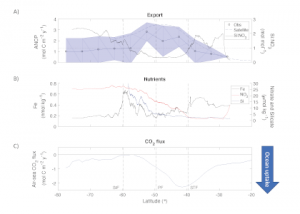
Read MoreThe Southern Ocean is a major player in driving global distributions of heat, carbon dioxide, and nutrients, making it key to ocean chemistry and the earth’s climate system. In the ocean, biological production and export of organic carbon are commonly linked to places with high nutrient availability. A recent paper, published in Global Biogeochemical Cycles, […]
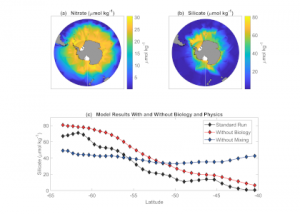
Read MoreIn the Southern Ocean, surface water silicate (SiO4) concentrations decline very quickly relative to nitrate concentrations along a northward gradient toward mode water formation regions on the northern edge (Figure 1a, b). These mode waters play a critical role in driving global nutrient concentrations, setting the biogeochemistry of low- and mid-latitude regions around the globe […]
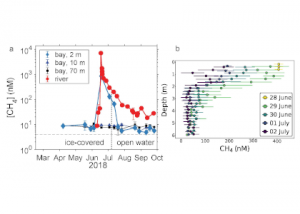
Read MoreRapid environmental changes in the Arctic will potentially alter the atmospheric emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases such as methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). A recent study on the Canadian Arctic published in Geophysical Research Letters reveals that spring meltwater delivery drives episodic outgassing events along the lake-river-bay continuum. This spring runoff period is not […]
Read More