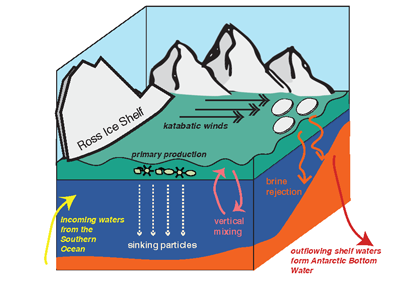
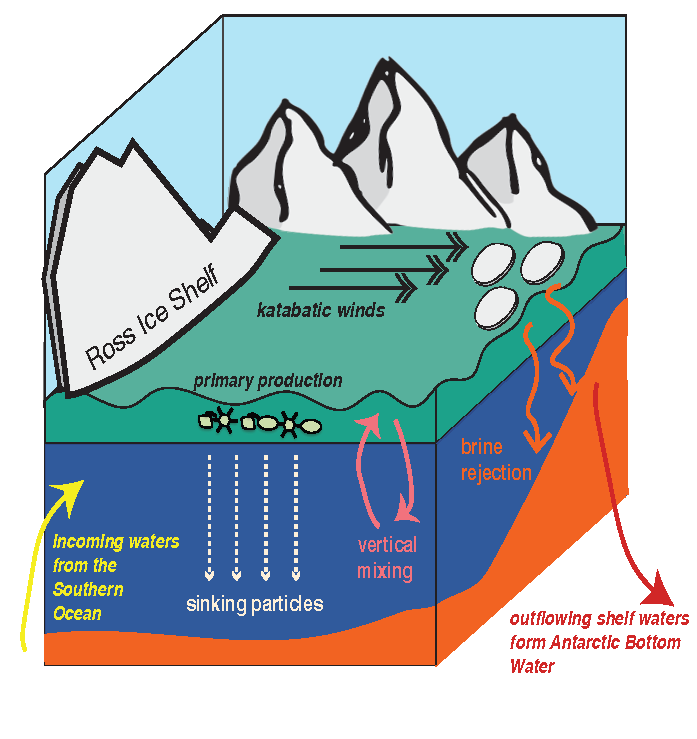
Studies of cruise observations in the Ross Sea are typically biased to a single or a few year(s), and long-term trends have predominantly come from satellites. Consequently, the in situ climatological patterns of nutrients and particulate matter have remained vague and unclear. What are the typical patterns of nutrients and particulate matter concentrations in the Ross Sea in spring and summer? How do these concentrations affect annual productivity estimates?
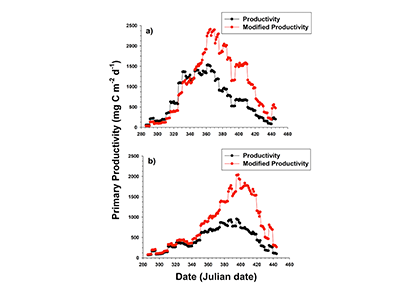
Patterns of nutrient and particulate matter in the Ross Sea can play a wide-ranging role in a productive region like the Ross Sea. Smith and Kaufman (2018) recently synthesized austral spring and summer (November to February) observations from 42 Ross Sea research cruises (1967-2016) to analyze broad biogeochemical patterns. The resulting climatologies revealed interesting seasonal patterns of nutrient uptake and particulate organic carbon (POC) to chlorophyll (chl) ratios (POC:chl). Temporal patterns in the nitrate and phosphate climatologies confirm the role of early spring haptophyte (Phaeocystis antarctica) growth, followed by limited nitrogen and phosphorus removal in summer. However, a notable increase in POC occurred later in summer that was largely independent of chlorophyll changes, resulting in a dramatic increase in POC:chl. A gradual decline in silicic acid concentrations throughout the summer, along with an increased occurrence of biogenic silica during this time suggest that diatoms may be responsible for this later POC spike. Revised estimates of primary productivity based on these observed climatological POC:chl ratios suggests that summer blooms may be a significant contributor to seasonal productivity, and that estimates of productivity based on satellite pigments underestimate annual production by at least 70% (Figure 1).
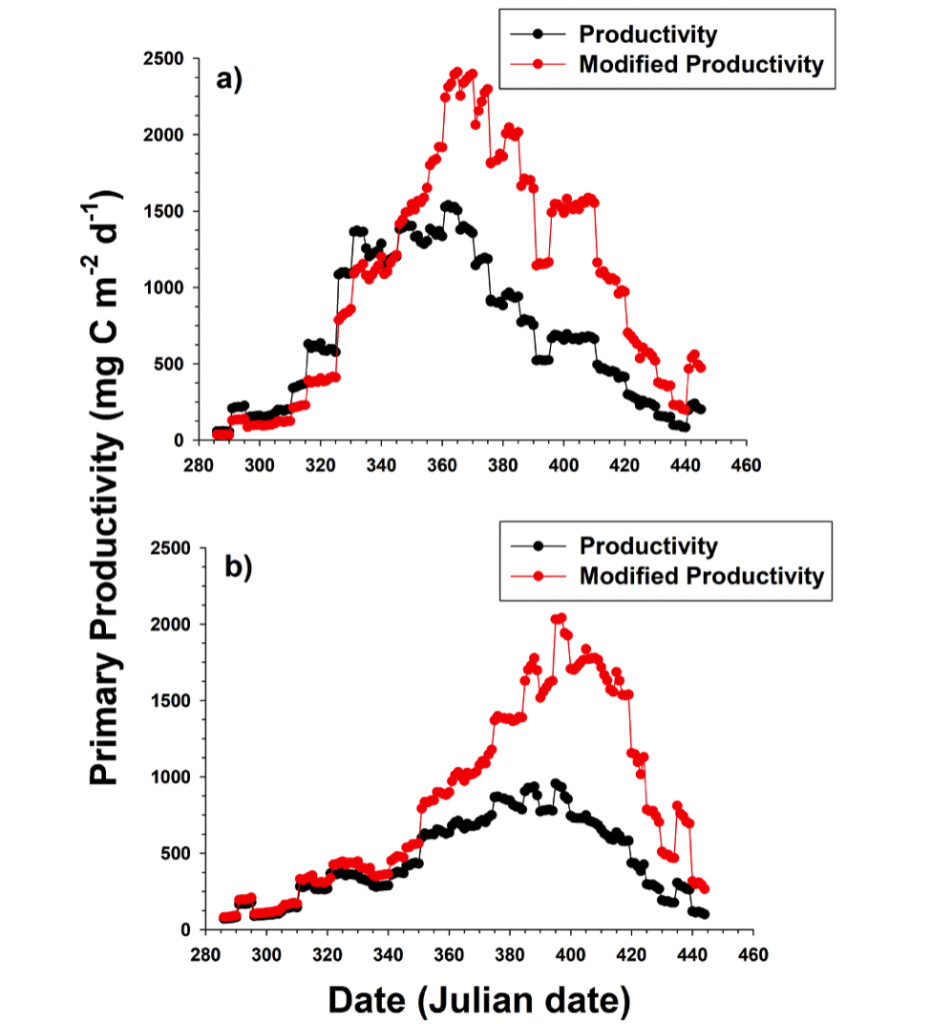
Figure 1. Bio-optical estimates of mean productivity using a constant POC:chl ratio (black dots and lines) and modified estimates of productivity using the monthly climatological POC:chl ratios (red dots and lines), in a) the Ross Sea polynya region and b) the western Ross Sea region.
By clarifying typical seasonal patterns of nutrient uptake and POC:chl, these climatologies underscore the biogeochemical importance of both spring haptophyte growth and previously underestimated summer diatom growth in the Ross Sea. Further investigation of the causes and consequences of elevated summer ratios is needed, as assessments of regional food webs and biogeochemical cycles depend on more accurate understanding of primary productivity patterns. Likewise, these results highlight the need for continued efforts to constrain satellite productivity estimates in the Ross Sea using in situ constituent ratios.
For other relevant work on seasonal biogeochemical patterns in the Ross Sea, please see https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2003.07.010. And for intra-seasonal estimates of particulate organic carbon to chlorophyll using gliders, please see: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2014.06.011.
Authors:
Walker O. Smith Jr. (VIMS, College of William and Mary)
Daniel E. Kaufman (VIMS, College of William and Mary; now at Chesapeake Research Consortium)