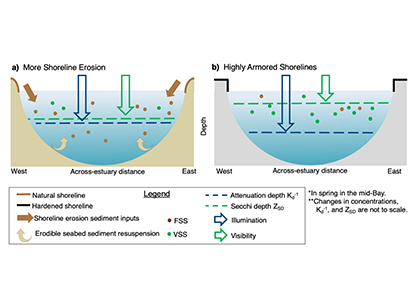
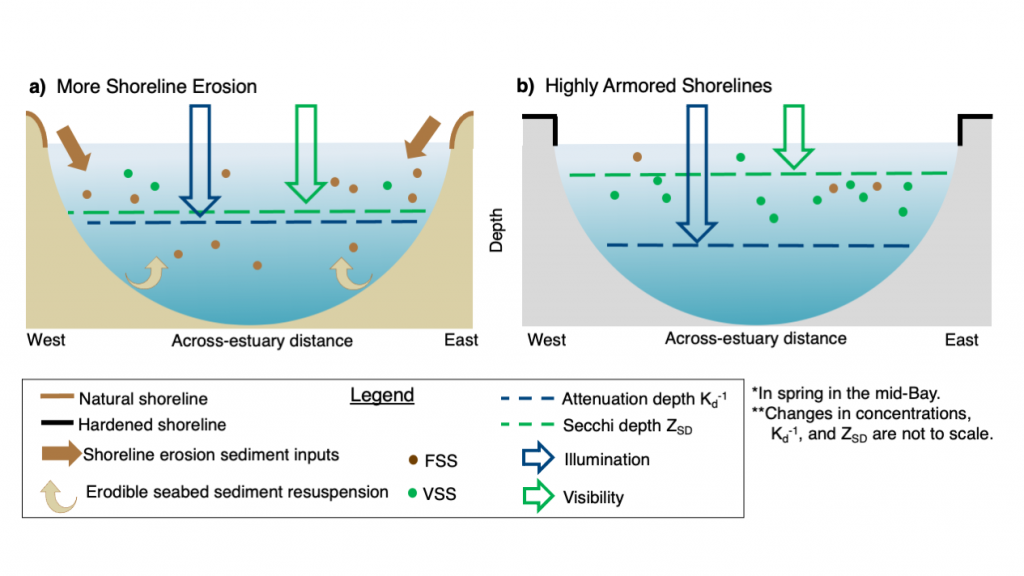
To maintain marine ecosystem health and human well-being, it is important to understand coastal water quality changes. Water clarity is a key component of water quality, which can be measured in situ by tools such as Secchi disks or by satellites with high spatial and temporal coverage. Coastal environments pose unique challenges to remote sensing, sometimes resulting in inaccurate estimates of water clarity.
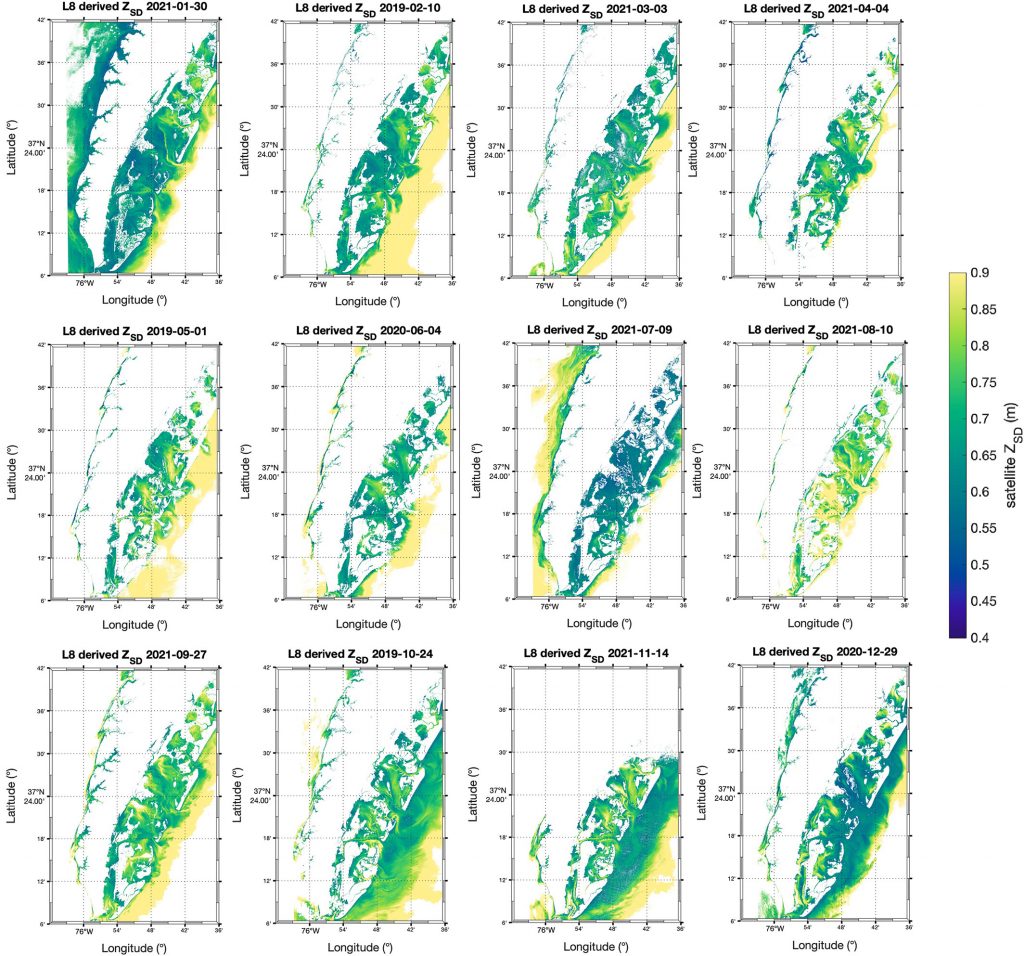
Figure caption: Maps of model-corrected Landsat-8 derived Secchi depths from monthly clear sky images (2019–2021).
In this study, we couple low-cost in situ methods (Secchi disk depths) with open-access, high-resolution satellite (Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2) data to improve estimates of water clarity in a shallow, turbid lagoon in Virginia, USA. Our model allows the retrieval of water clarity data across an entire water body and when field measurements are unavailable. This approach can be implemented in dynamic coastal water bodies with limited in situ measurements (e.g., as part of routine water quality monitoring). This can improve our understanding of water clarity changes and their drivers to better predict how water quality may change in the future. Improved water clarity predictions can lead to better coastal ecosystem management and human well-being.
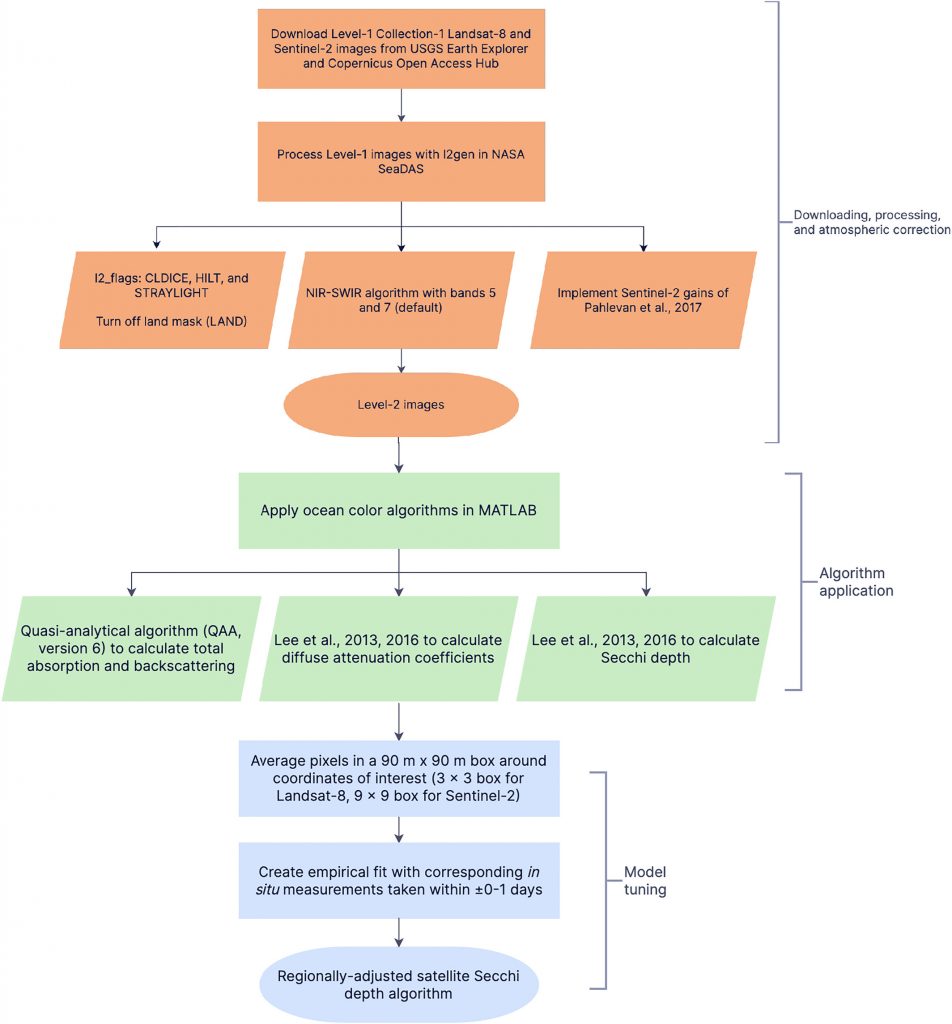
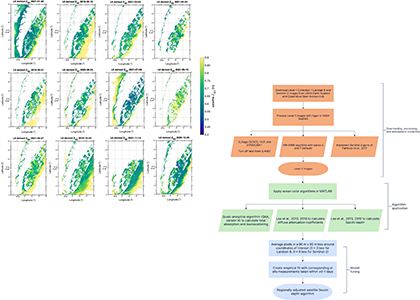
Figure caption: Workflow for obtaining Secchi disk depth with l2gen in NASA SeaDAS, bio-optical algorithms, and empirical adjustments.
Authors
Sarah E. Lang (University of Rhode Island’s Graduate School of Oceanography)
Kelly M.A. Luis (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology)
Scott C. Doney (University of Virginia)
Olivia Cronin-Golomb (University of Virginia)
Max C.N. Castorani (University of Virginia)
Twitter / Mastodon
@sarah_langsat8 on Twitter
@kelly_luis1 on Twitter
@scottdoney@universeodon.com on Mastodon
@ocronin_golomb on Twitter
@MaxCastorani on Twitter