If you would like to have your recent publications featured on the OCB website please contact ocb_news@whoi.edu. View our guidelines for writing a New OCB Research post.
Only about half of human-made CO2 emissions remain in the atmosphere and drive global warming. The other half has so far been said to be taken up in roughly equal amounts by the biosphere on land and by physical-chemical processes in the ocean. In equal amounts? In a new assessment, Friedlingstein et al. reassess the […]
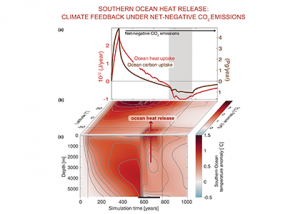
Read MoreThe ocean stores vast amounts of heat and carbon under anthropogenic CO₂ emissions, but its behavior under net-negative emission scenarios remains poorly understood. Here we use an Earth System Model of intermediate complexity and show results of an idealized future climate scenario that includes sustained net-negative emissions over centuries. After gradual global cooling, the model […]
Read MoreA Microbial Conveyor Belt Beneath the South Pacific
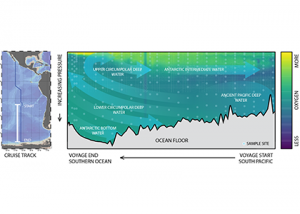
Global overturning circulation is a planetary conveyor belt: dense waters sink around Antarctica, spread through the deep ocean for centuries, and eventually rise elsewhere, redistributing heat, nutrients, and carbon. But how does this slow, pervasive movement of water impact marine microbes? To find out, researchers collected over 300 water samples spanning the full depth […]
Read MoreMarine plant metabolites give marine microbes gas
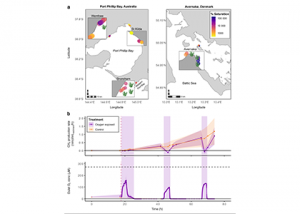
A recent study in Nature Geosciences observed high concentrations of methane overlying permeable (sand) sand sediments in bays in Denmark and Australia. These environments are not one would expect to see methane because they are highly oxygenated and the high concentrations of sulfate in seawater typically inhibit methanogenesis. The authors showed that the methane was […]
Read MoreFrom smoke to sea, how wildfire ash reshapes ocean microbial life
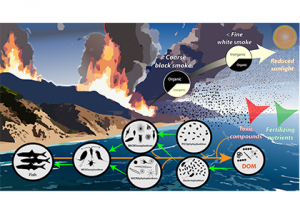
When wildfire smoke drifts over the ocean, what happens beneath the waves? As wildfires change in nature and become more frequent, it’s increasingly important to understand how ash deposition affects the ocean’s smallest, yet most essential, inhabitants. In a recent study, the authors investigated how wildfire ash leachate influences coastal microbial communities. Through field incubations […]
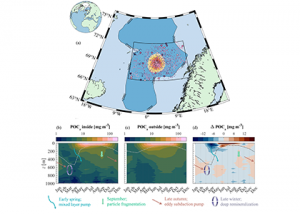
Read MoreHow does a persistent eddy impact the biological carbon pump?
The Lofoten Basin Eddy (LBE) is a unique and persistent anticyclonic feature of the Norwegian Sea that stirs the water column year-round. However, its impact on biogeochemical processes that influence region carbon storage, including carbon fixation, particle aggregation and fragmentation, and remineralization, has remained largely unknown. Using 12 years of data from Biogeochemical-Argo floats and […]
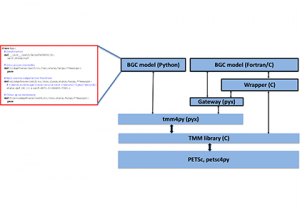
Read MoreHave you ever wondered what life would be like if you could write and run complex biogeochemical models easily and conveniently in Python? Wonder no more. In a paper published in J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst., Samar Khatiwala (2025; see reference below) describes tmm4py, a new software to enable efficient, global scale biogeochemical modelling in […]
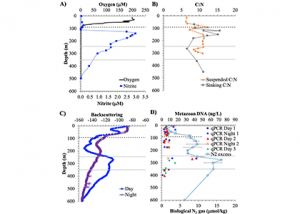
Read MoreDiel Vertically Migrating Zooplankton that spend their day in an Oxygen Deficient Zone to avoid predators are a previously ignored source of organic matter for N2 producing bacteria. A recent study in GBC, examined biogeochemical cycling in the offshore Eastern Tropical North Pacific Oxygen Deficient Zone. They found that the daytime maximum in backscattering, used […]
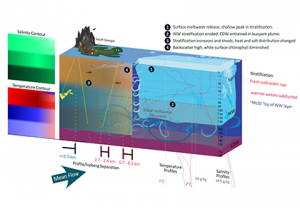
Read MoreIceberg meltwater induces mixing which erodes upper-ocean layers. This supplies nutrients, both released from the iceberg and entrained from deeper waters, to surface waters which stimulates phytoplankton growth. Meltwater from the base, sidewalls and surface of giant icebergs influences upper ocean stratification and mixing. Containing a substantial micro-nutrient load, (incorporating nutrient-rich deep waters along with […]
Read MoreThe ocean’s biological carbon pump (BCP) plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. But how efficiently does it transport carbon to the deep? It has been difficult to answer this question because observations are sparse, labor-intensive, and the uncertainties of the BCP’s magnitude, which are nearly equivalent to human emissions. Fortunately, autonomous vehicles unlock […]
Read More