Relative to their surface area, coastal regions represent some of the largest carbon fluxes in the global ocean, driven by numerous physical, chemical and biological processes. Coastal systems also experience human impacts that affect carbon cycling, which has large socioeconomic implications. The highly dynamic nature of these systems necessitates observing approaches and numerical methods that can both capture high-frequency variability and delineate long-term trends.
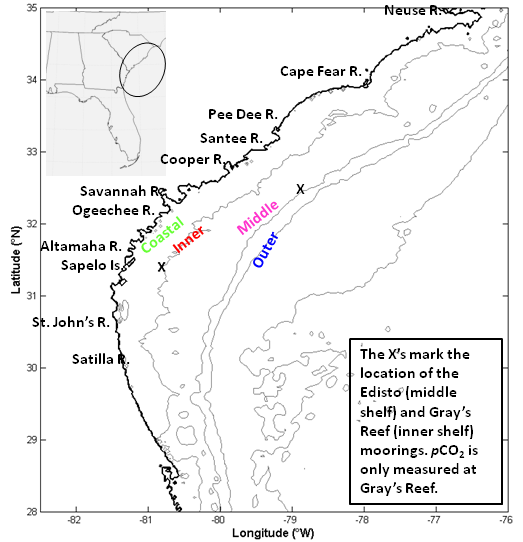
Figure 1: The South Atlantic Bight (SAB) was divided into four sections using isobaths: the coastal zone (0 to 15 m), the inner shelf (15 to 30 m), the middle shelf (30 to 60 m), and the outer shelf (60 m and beyond). The X’s indicate the locations of the Gray’s Reef mooring (southern X) and the Edisto mooring (northern X).
In two recent studies using mooring- and ship-based ocean CO2 system data, authors observed that pCO2 is increasing from the coastal zone to the outer shelf of the South Atlantic Bight at rates greater than the global average oceanic and atmospheric increase (~1.8 µatm y-1). In recent publications in Continental Shelf Research and JGR-Oceans, the authors analyzed pCO2 data from 46 cruises (1991-2016) using a novel linear regression technique to remove the seasonal signal, revealing an increase in pCO2 of 3.0-3.7 µatm y-1 on the outer and inner shelf, respectively. Using a Generalized Additive Mixed Model (GAMM) approach for trend analysis, authors observed that the rates of increase were slightly higher than the deseasonalization technique, yielding pCO2 increases of 3.3 to 4.5 µatm y-1 on the outer and inner shelf, respectively. The reported pCO2 increases result in potential pH decreases of -0.003 to -0.004 units y-1.
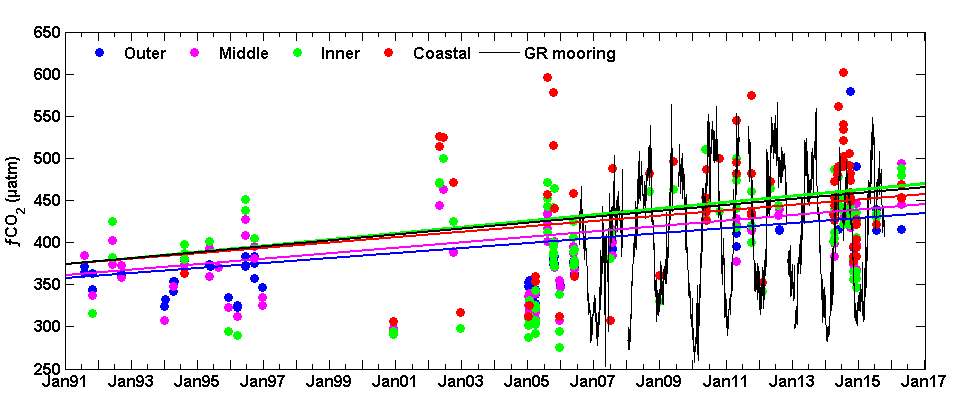
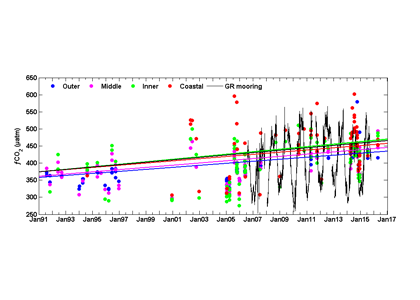
Figure 2: The time series of fCO2 in the four regions of the SAB (cruise observations) and from the Gray’s Reef mooring on the inner shelf indicate an increase across the shelf. These data are the observed values, however, the trend lines for each time series are calculated using deseasonalized values using the reference year method.
Analysis of the pCO2 time-series from the Gray’s Reef mooring (using a NOAA Moored Autonomous pCO2 system from July 2006 -July 2015) yielded a rate of increase (3.5 ± 0.9 µatm y-1) that was comparable to the cruise data on the inner shelf (3.7 ± 2.2 and 4.5 ± 0.6 µatm y-1, linear and GAMM methods, respectively). Validation data collected at the mooring suggest that underway data from cruises and the moored data are comparable. Neither thermal processes nor atmospheric dissolution (the primary driver of oceanic acidification) can explain the observed pCO2 increase and concurrent pH decrease across the shelf. Unlike the middle and outer shelves, where an increase in SST could account for up to 1.1 µatm y-1 of the observed pCO2 trend, there is no thermal influence in the coastal zone and inner shelf. While 1.8 µatm y-1 could be attributed to the global average atmospheric increase, the remainder is likely due to transport from coastal marshes and in situ biological processes. As the authors have shown, the increasing coastal and oceanic trend in pCO2 can lead to a decrease in pH, especially if there is no increase in buffering capacity. More acidic waters can have a long term affect on coastal ecosystem services and biota.
Also see Eos Editor’s Vox on this research by Peter Brewer https://eos.org/editors-vox/coastal-ocean-warming-adds-to-co2-burden
Authors:
Multidecadal fCO2 Increase Along the United States Southeast Coastal Margin (JGR-Oceans)
Janet J. Reimer (University of Delaware)
Hongjie Wang (Texas A &M University – Corpus Christi)
Rodrigo Vargas (University of Delaware)
Wei-Jun Cai (University of Delaware)
And
Time series pCO2 at a coastal mooring: Internal consistency, seasonal cycles, and interannual variability (Continental Shelf Research)
Janet J. Reimer (University of Delaware)
Wei-Jun Cai (University of Delaware; University of Georgia)
Liang Xue (University of Delaware; First Institute of Oceanography, China)
Rodrigo Vargas (University of Delaware)
Scott Noakes (University of Georgia)
Xinping Hu (Texas A &M University – Corpus Christi)
Sergio R. Signorini (Science Applications International Corporation)
Jeremy T. Mathis (NOAA Arctic Research Program)
Richard A. Feely (NOAA Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory)
Adrienne J. Sutton (NOAA Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory; University of Washington)
Christopher Sabine (University of Hawaii Manoa)
Sylvia Musielewicz (NOAA Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory; University of Washington)
Baoshan Chen (University of Delaware; University of Georgia)
Rik Wanninkhof (NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory)