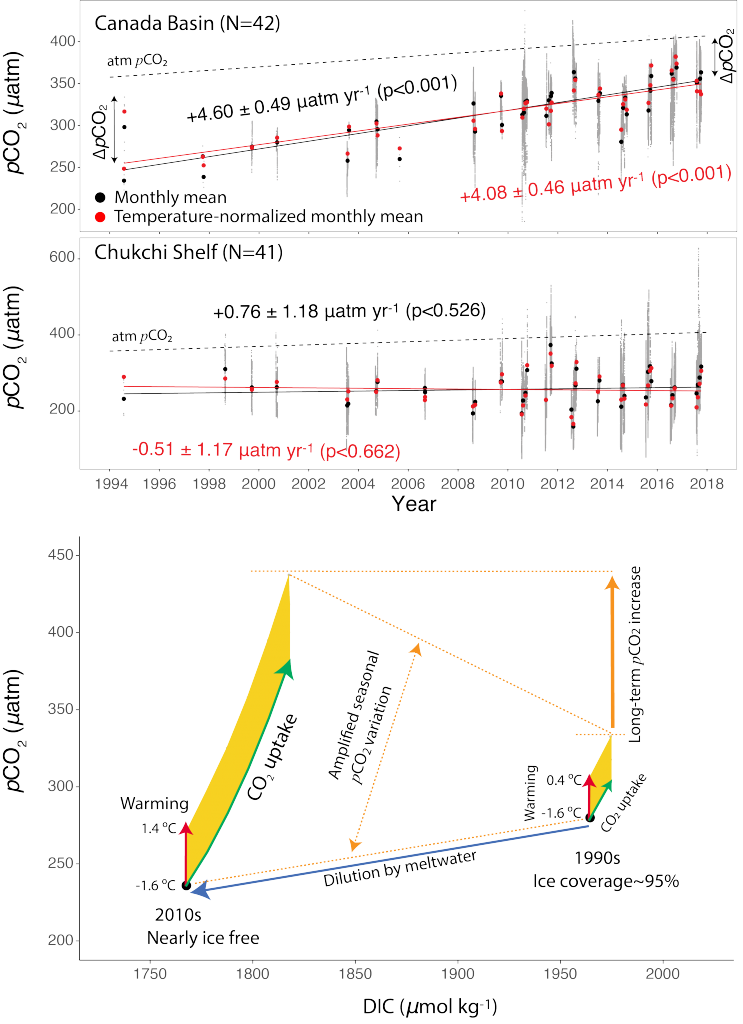
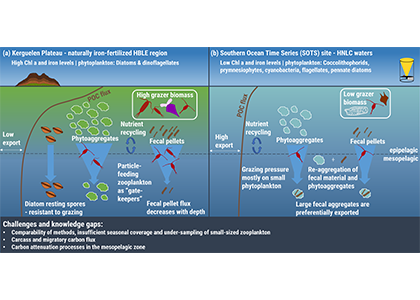
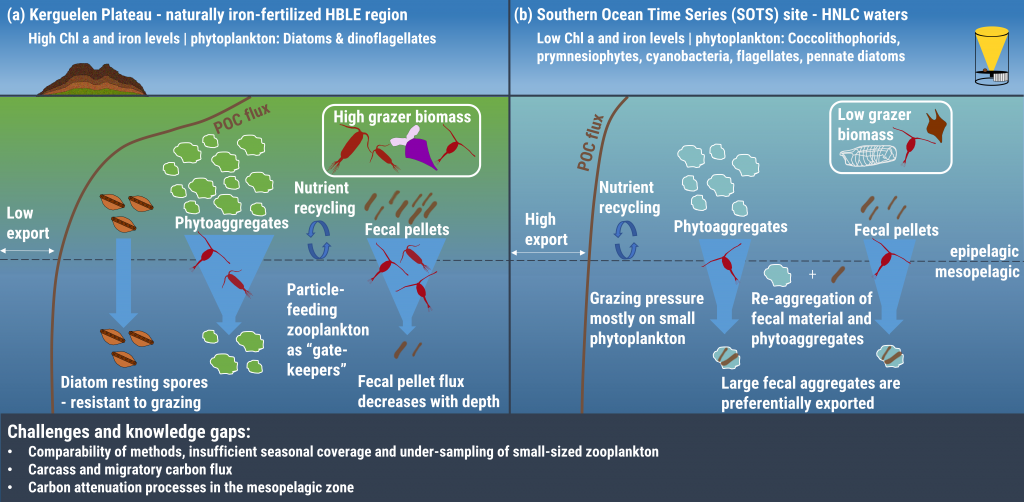
The marine biological pump (BP) plays a crucial role in regulating earth’s atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide levels by transferring carbon fixed by primary producers into the ocean interior and marine sediments, thereby controlling the habitability of our planet. The rise of multicellular life and eukaryotic algae in the ocean about 700 million years ago would likely have influenced the physical characteristics of oceanic aggregates (e.g., sinking rate), yet the magnitude of the impact this biological innovation had on the efficiency of BP is unknown.
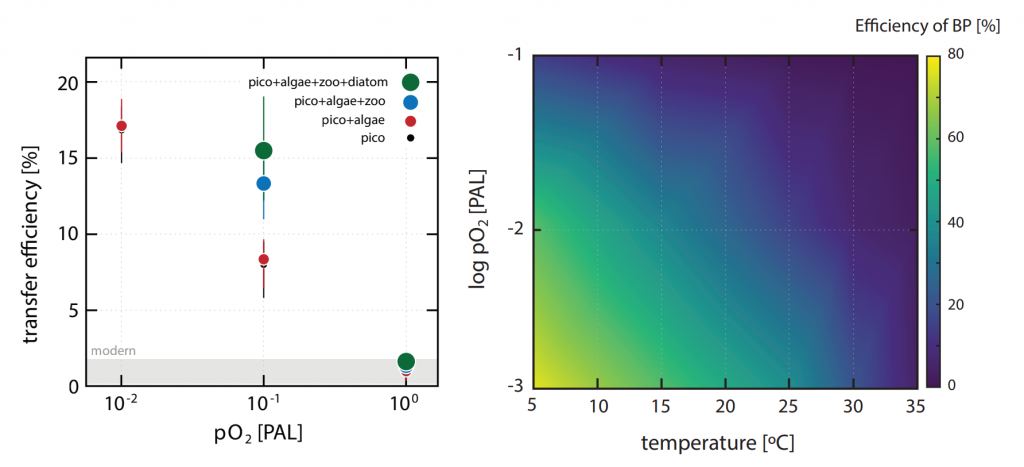
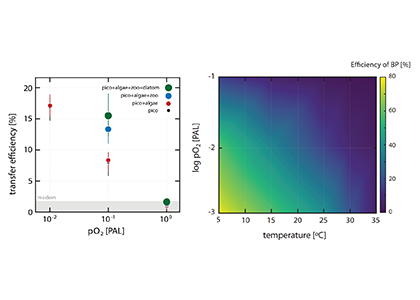
Figure. 1. The impact of biological innovations (left) and environmental factors (atmospheric oxygen level and seawater temperature; right) on the efficiency of marine biological pump (BP). Temperatures are ocean surface temperatures (SST), and atmospheric pO2 is shown relative to the present atmospheric level (PAL). The BP efficiency is calculated as the fraction of carbon exported from the surface ocean that is delivered to the sediment-water interface. The results indicate that evolution of larger sized algae and zooplanktons has little influence on the long-term evolution of biological pump (left panel). The change in the atmospheric oxygen level and seawater surface temperature as environmental factors, on the other hand, have a stronger leverage on the efficiency of biological pump (right panel).
The authors of a recent paper in Nature Geoscience constructed a particle-based stochastic model to explore the change in the efficiency of the BP in response to biological and physical changes in the ocean over geologic time. The model calculates the age of organic particles in each aggregate based on their sinking rates, and considers the impact of primary producer cell size, aggregation, temperature, dust flux, biomineralization, ballasting by mineral phases, oxygen, and the fractal geometry (porosity) of aggregates. The model results demonstrate that while the rise of larger-sized eukaryotes led to an increase in the average sinking rate of oceanic aggregates, its impact on BP efficiency was minor. The evolution of zooplankton (with daily vertical migration in the water column) had a larger impact on the carbon transfer into the ocean interior. But results suggest that environmental factors most strongly affected the marine carbon pump efficiency. Specifically, increased ocean temperatures and greater atmospheric oxygen abundance led to a significant decrease in the efficiency of the BP. Cumulatively, these results suggest that while major biological innovations influenced the efficiency of BP, the long-term evolution of the marine carbon pump was primarily controlled by environmental drivers such as climate cooling and warming. By enhancing the rate of heterotrophic microbial degradation, our results suggest that the anthropogenically-driven global warming can result in a less efficient BP with reduced power of marine ecosystem in sequestering carbon from the atmosphere.
Authors:
Mojtaba Fakhraee (Yale University, Georgia Tech, and NASA Astrobiology Institute)
Noah J. Planavsky (Yale University, and NASA Astrobiology Institute)
Christopher T. Reinhard (Georgia Tech, and NASA Astrobiology Institute)