Nitrifying microbes are the most abundant chemoautotrophs in the dark ocean. Though better known for their role in the nitrogen cycle, they also fix dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) into biomass and thus play an important role in the global carbon cycle. The release of organic compounds by these microbes may represent an as-yet unaccounted for source of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) available to heterotrophic marine food webs. Quantifying how much DIC these microbes fix and release again into the ambient seawater is critical to a complete understanding of the carbon cycle in the deep ocean.
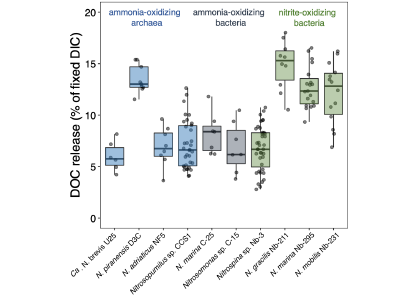
To address this knowledge gap, a recent study grew ten diverse nitrifier cultures and measured their cellular carbon (C) content, DIC fixation yields and DOC release rates. The results indicate that nitrifiers release between 5 and 15% of their recently fixed DIC as DOC (Figure 1). This would equate to global ocean fluxes of 0.006–0.02 Pg C yr−.
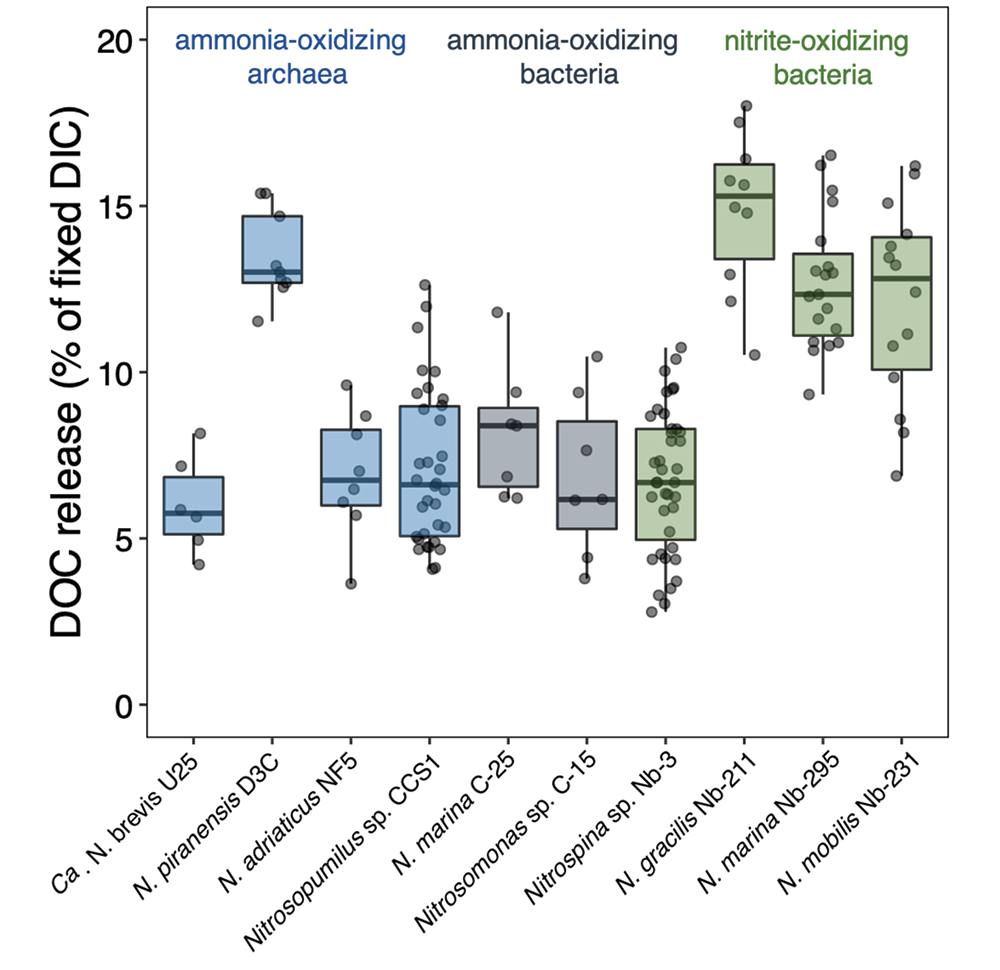
Figure 1. DOC release by ten different chemoautotrophic nitrifying (ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing) microbes. The diversity of marine nitrifiers used in this study comprises all genera currently available as axenic cultures. Species and strain names are given for completeness.
Our results provide values for biogeochemical models of the global carbon cycle, and help to further constrain the relationship between C and N fluxes in the nitrification process. Elucidating the lability and fate of carbon released by nitrifiers will be the crucial next step to understand its implications for marine food-web functioning and the biological sequestration of carbon in the ocean.
Authors:
Barbara Bayer (University of California, Santa Barbara and University of Vienna)
Kelsey McBeain (University of California, Santa Barbara)
Craig A. Carlson (University of California, Santa Barbara)
Alyson E. Santoro (University of California, Santa Barbara)