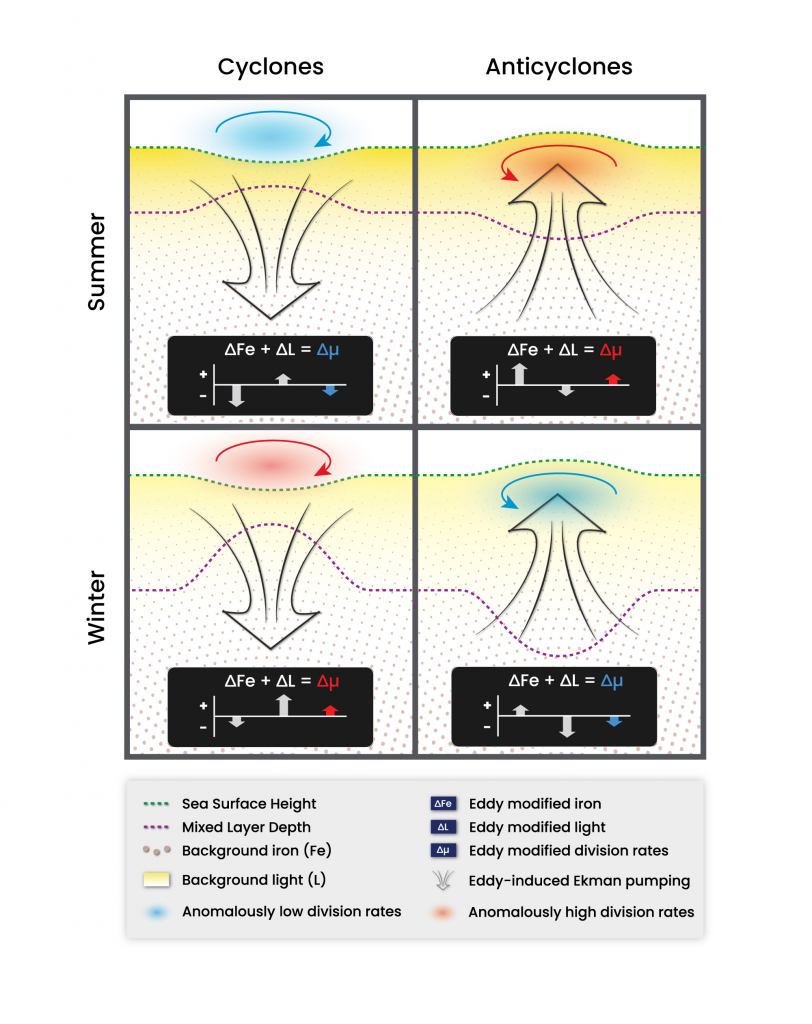
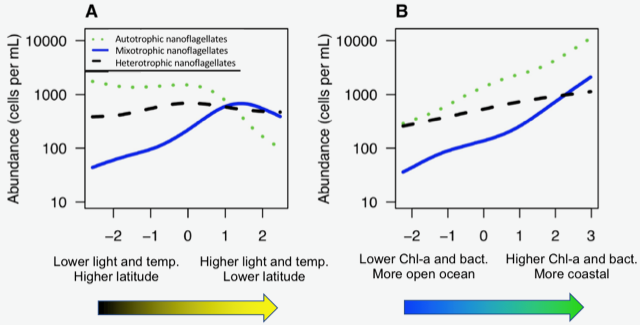
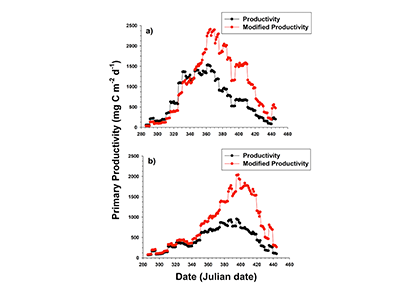
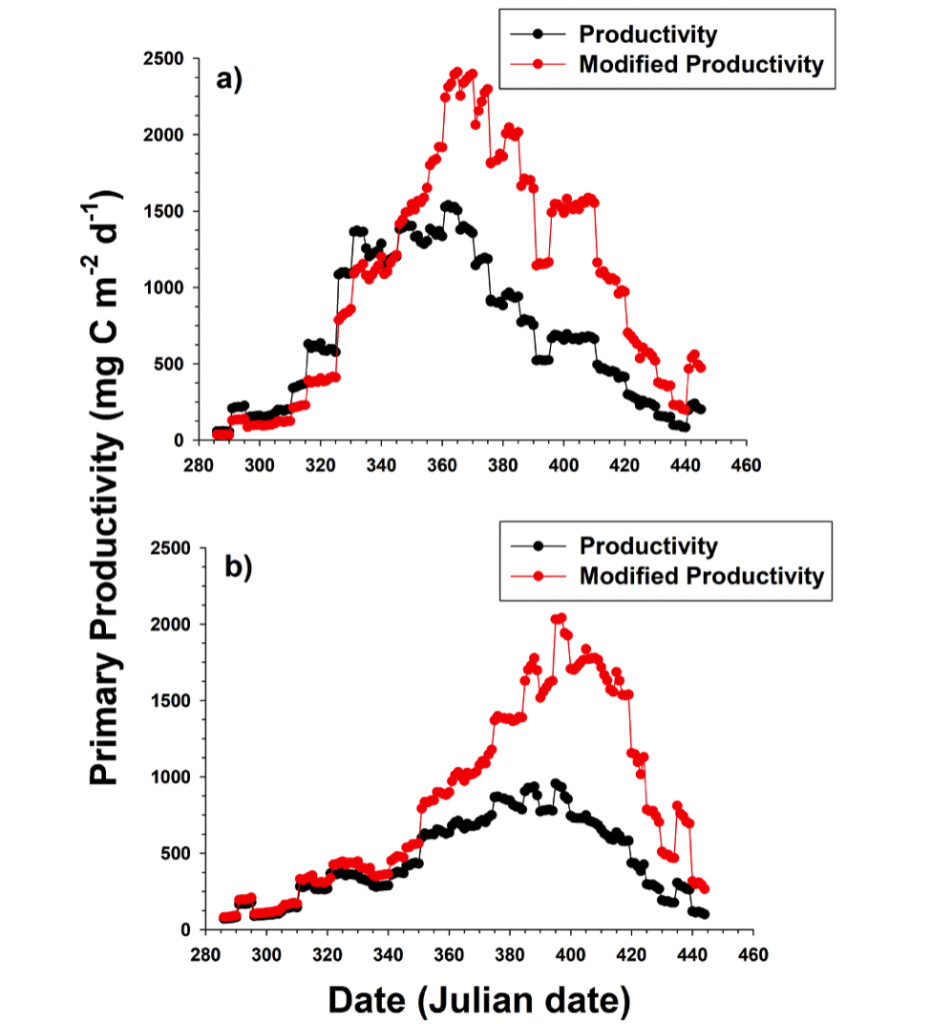
Unlike most remote sensing products, Net Primary Production (NPP) is computed under clouds. Since satellites can’t see through clouds, NPP models rely on clear-sky observations, interpolate model inputs, and assume that phytoplankton behavior stays the same, regardless of light conditions.
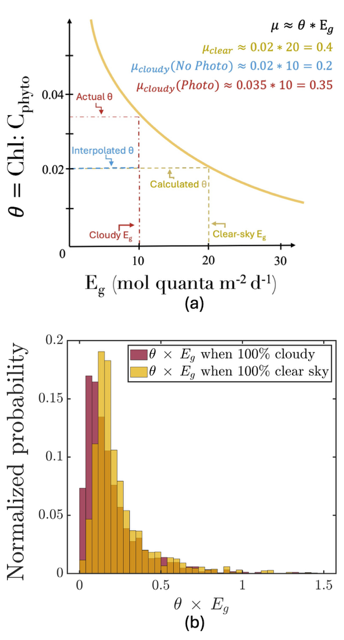
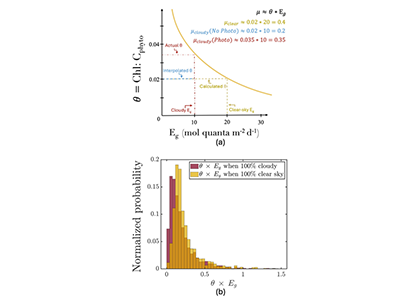
Figure caption: (a) Schematic of the photoacclimation process. In yellow, a standard photoacclimation curve where θ (the chlorophyll to phytoplankton carbon ratio), adjusts as a function of light in the mixed layer (Eg). In blue, the schematic when we do not consider photoacclimation under cloud: Eg is reduced due to cloud-cover, but θ remains the same as it was under cloud, resulting in a strongly reduced μ (a proxy for growth rate). When considering photoacclimation under clouds (red), θ increases because of a reduced Eg, resulting in a μcloudy(photo) > μcloudy(no photo). (b) Histogram of the distribution of θ*Eg (a proxy for growth rate) from BGC-Argo floats separated by whether under cloudy (red) or clear (yellow) skies.
But phytoplankton are known to photoacclimate, adjusting their internal chlorophyll to carbon ratio in response to changes in light. In this study published in GRL we used data from BGC-Argo floats to show that this acclimation occurs consistently under both clear and cloudy skies across the global ocean. Despite reduced light, phytoplankton maintain similar growth rates, suggesting that current estimates of NPP may be biased low when cloud cover is present.
Recognizing and correcting this bias could improve satellite-based NPP estimates, particularly in persistently cloudy regions like the Southern Ocean or eastern boundary upwelling zones. This, in turn, would refine models of the ocean’s biological carbon pump, leading to better projections of CO₂ uptake and export.
Authors
Charlotte Begouen Demeaux (Univ Maine)
Emmanuel Boss (Univ Maine)
Jason R. Graf (Oregon State Univ)
Michael J. Behrenfeld (Oregon State Univ)
Toby Westberry (Oregon State Univ)