If you would like to have your recent publications featured on the OCB website please contact ocb_news@whoi.edu. View our guidelines for writing a New OCB Research post.
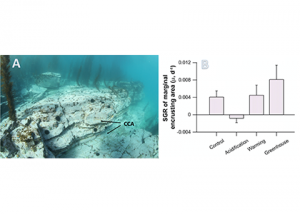
Seawater carbonate chemistry has been altered by dramatic increases in anthropogenic CO2 release and global temperatures, leading to significant changes in rocky shore habitats and the metabolism of most marine organisms. There has been recent interest in how these anthropogenic stresses affect crustose coralline algae (CCA) communities because CCA photosynthesis and calcification are directly influenced […]
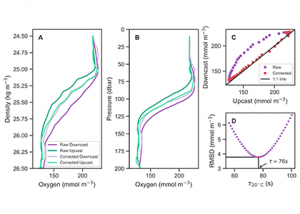
Read MoreDespite its fundamental importance to the global carbon cycle, climate, and marine ecosystems, oceanic primary production is grossly under-sampled. Autonomous platforms represent an important frontier for expanding measurements of marine primary productivity in time and space, but this requires the establishment of robust, standardized methods to obtain reliable data from these platforms. Using data from […]
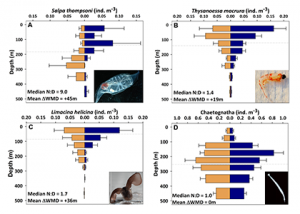
Read MoreSunrise and sunset are the main cues driving zooplankton diel vertical migration (DVM) throughout the world’s oceans. These marine animals balance the trade-off between feeding in surface waters at night and avoiding predation during the day at depth. Near-constant daylight during polar summer was assumed to dampen these daily migrations. In a recent paper published […]
Read MoreOcean temperature extreme events such as marine heatwaves are expected to intensify in coming decades due to anthropogenic warming. Although the effects of marine heatwaves on large plants and animals are becoming well documented, little is known about how these warming events will impact microbes that regulate key biogeochemical processes such as ocean carbon uptake […]
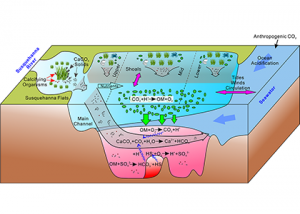
Read MoreOcean acidification is often enhanced by eutrophication and subsequent hypoxia and anoxia in coastal waters, which collectively threaten marine organisms and ecosystems. Acidification is particularly of concern for organisms that form shells and skeletons from calcium carbonate (CaCO3) such as commercially important shellfish species. Given that CaCO3 mineral dissolution can increase the total alkalinity of […]
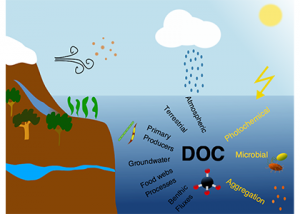
Read MoreThe dissolved organic carbon (DOC) pool is vital for the functioning of marine ecosystems. DOC fuels marine food webs and is a cornerstone of the earth’s carbon cycle. As one of the largest pools of organic matter on the planet, disruptions to marine DOC cycling driven by climate and environmental global changes can impact air-sea […]
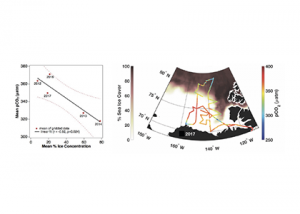
Read MoreLoss of Arctic Ocean ice cover is altering the carbon cycle in ways that are not well understood. Effectively “popping the top off” the Arctic Ocean, ice loss exposes the sea surface to warming and exchange of CO2 with the atmosphere. These processes are expected to increase CO2 levels in the Arctic Ocean, changing its […]
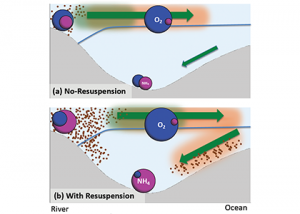
Read MoreSediment processes, including resuspension and transport, affect water quality in estuaries by altering light attenuation, primary productivity, and organic matter remineralization, which then influence oxygen and nitrogen dynamics. In a recent paper published in Estuaries and Coasts, the authors quantified the degree to which sediment resuspension and transport affected estuarine biogeochemistry by implementing a coupled […]
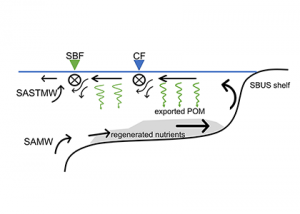
Read MoreThe southern Benguela upwelling system (SBUS) off southwest Africa is an exceptionally fertile ocean region that supports valuable commercial fisheries. The productivity of this system derives from the upwelling of nutrient-rich Subantarctic Mode Water, and from the concurrent entrainment of nutrients regenerated proximately on the expansive continental shelf. The SBUS is prone to severe seasonal […]
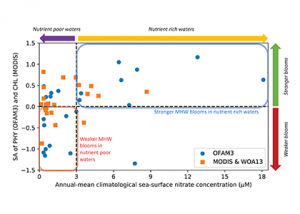
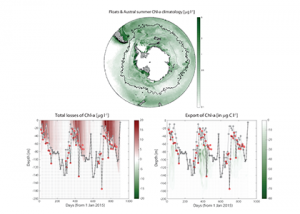
Read MoreMore observations are needed to constrain the relative roles of physical (advection), biogeochemical (downward export), and ecological (grazing and biological losses) processes in driving the fate of phytoplankton blooms in Southern Ocean waters. In a recent paper published in Nature Communications, authors used seven Biogeochemical Argo (BGC-Argo) floats that vertically profiled the upper ocean every […]
Read More