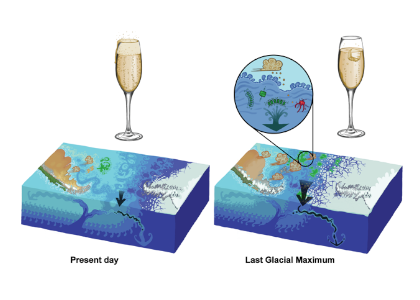
During the Last Glacial Maximum (~20,000 years ago, LGM) sediment data show that the deep ocean had lower dissolved oxygen (O2) concentrations than the preindustrial ocean, despite cooler temperatures of this period increasing O2 solubility in sea water.
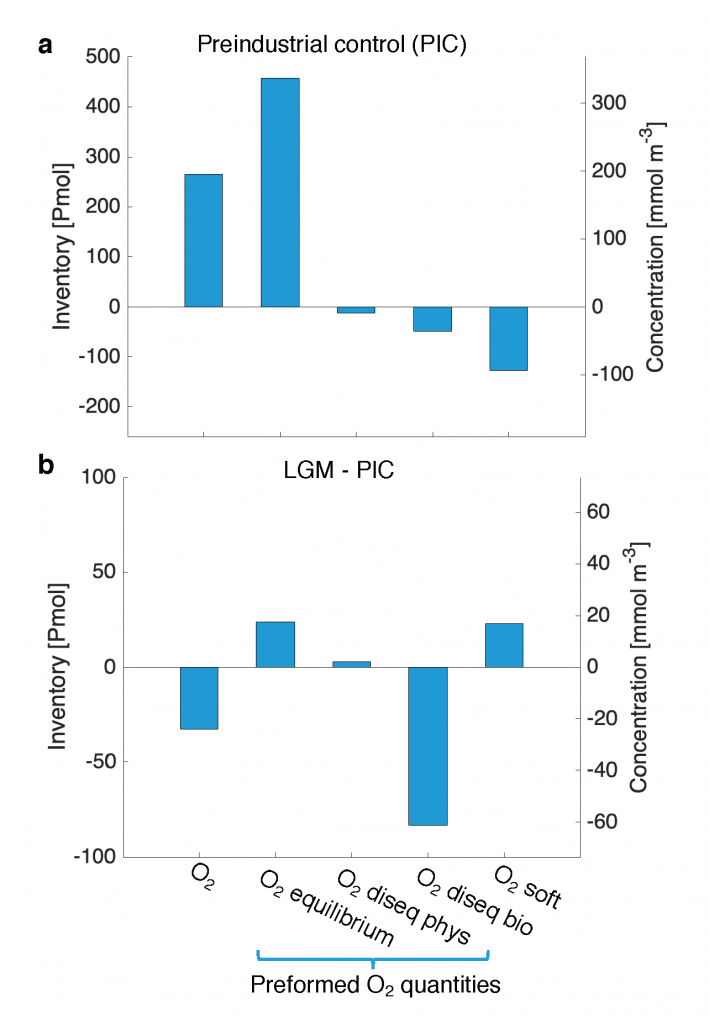
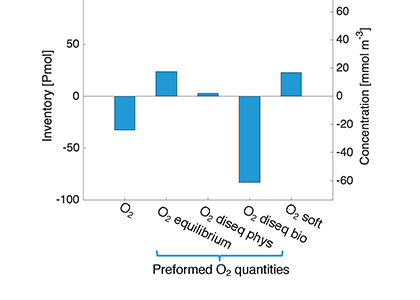
Figure 1. a) Whole ocean inventory of the O2 components in the preindustrial control (PIC): total O2 (O2); the preformed components equilibrium O2 (O2 equilibrium), physical disequilibrium O2 (O2 diseq phys) and biologically-mediated disequilibrium (O2 diseq bio); and O2 respired from soft-tissue (O2 soft). b) The difference in whole ocean inventory of O2 components between the LGM and PIC simulations.
In a study published in Nature Geoscience, the authors provide one of the first explanations for glacial deoxygenation. The authors combined a data-constrained model of the preindustrial (PIC) and LGM ocean with a novel decomposition of O2 to assess the processes affecting the oceanic distribution of oxygen. The decomposition allowed for the preformed disequilibrium O2—the amount of oxygen that deviates from its solubility equilibrium value when at the surface—to be tracked, along with other contributions such as the O2 consumed by bacterial respiration of organic matter. In the preindustrial ocean, a third of the subsurface oxygen deficit was a result of disequilibrium rather than oxygen consumed by bacteria. This contradicts previous assumptions (Figure 1a). Nearly 80% of the disequilibrium resulted from upwelling waters, depleted in O2 due to respiration, not fully equilibrating before re-subduction into the ocean interior. This effect was even greater during the LGM (Figure 1b). The authors attributed this largely to the widespread presence of sea ice—which acts as a cap on the surface preventing the water from gaining oxygen from the atmosphere—in the ocean around Antarctica, with a smaller contribution from iron fertilization.
This study provides one of the first mechanistic explanations for LGM deep ocean deoxygenation. As the ocean is currently losing oxygen due to warming, the effect of other processes, including sea ice changes, could prove important for understanding long-term ocean oxygenation changes.
Authors
Ellen Cliff (University of Oxford)
Samar Khatiwala (University of Oxford)
Andreas Schmittner (Oregon State University)