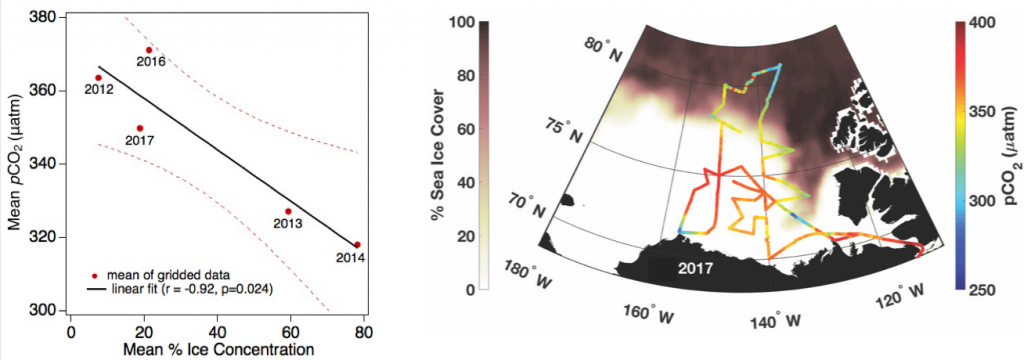
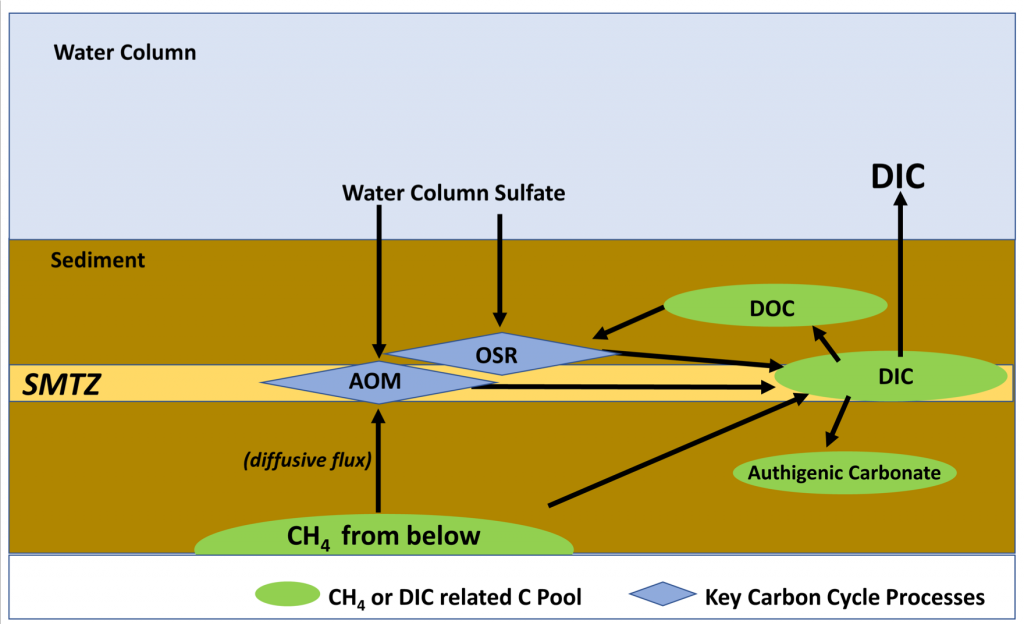
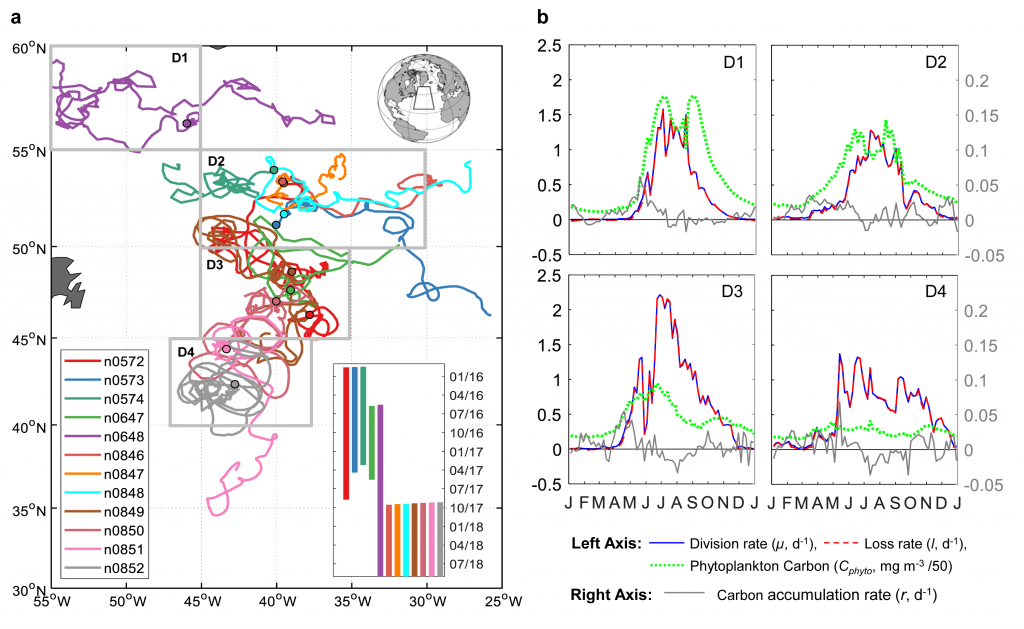
Carbon export from the surface into the deep ocean via the biological pump is a significant sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide. The relative contributions of sinking particles—particulate organic carbon (POC) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC)—to the total export affect the efficiency of carbon export.
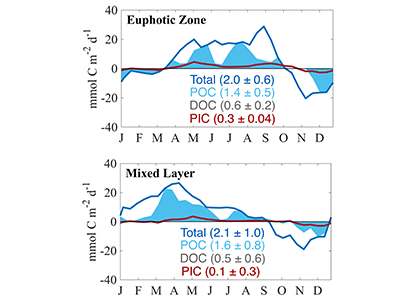
In a recent study published in Global Biogeochemical Cycles, the authors used measurements from biogeochemical profiling floats in the Northeast Pacific from 2009 to 2017 to estimate net community production (NCP), an analog for carbon export. In order to close three tracer budgets (nitrate, dissolved inorganic carbon, and total alkalinity), the authors combined these float measurements with data from the Ocean Station Papa mooring and recently developed algorithms for carbonate system parameters. By constraining end-member nutrient ratios of the POC and DOC produced, this multi-tracer approach was used to estimate regional NCP across multiple depth horizons throughout the annual cycle, partition NCP into the POC and DOC contributions, and calculate particulate inorganic carbon (PIC) production, a known ballast material for sinking particles (Figure 1). The authors also estimated POC attenuation with depth, POC export across deeper horizons, and in situ export efficiency via a particle backscatter-based approach.
With the advent of “fully-loaded” biogeochemical profiling floats equipped with nitrate, oxygen, pH and bio-optical sensors, this approach may be used to assess the magnitude and efficiency of carbon export in other ocean regions from a single platform, which will greatly reduce the risks and costs associated with traditional ship-based measurements, while broadening the spatiotemporal scales of observation.
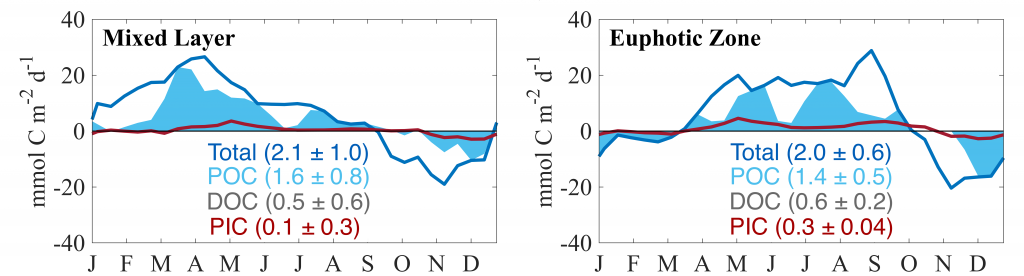
Figure caption: Climatological mean NCP (blue line) over the entire study period (2009-2017); the POC portion of NCP (filled blue area), the DOC portion (white space) and PIC production rate (red line), in the mixed layer (left), and the euphotic zone (right). The numbers in parentheses are the integrated annual NCP rates for each curve and uncertainty reported was determined using a Monte Carlo approach.
Authors:
William Haskell (MBARI, now Mote Marine Laboratory)
Andrea Fassbender (MBARI, now PMEL)
Jacki Long (MBARI)
Joshua Plant (MBARI)