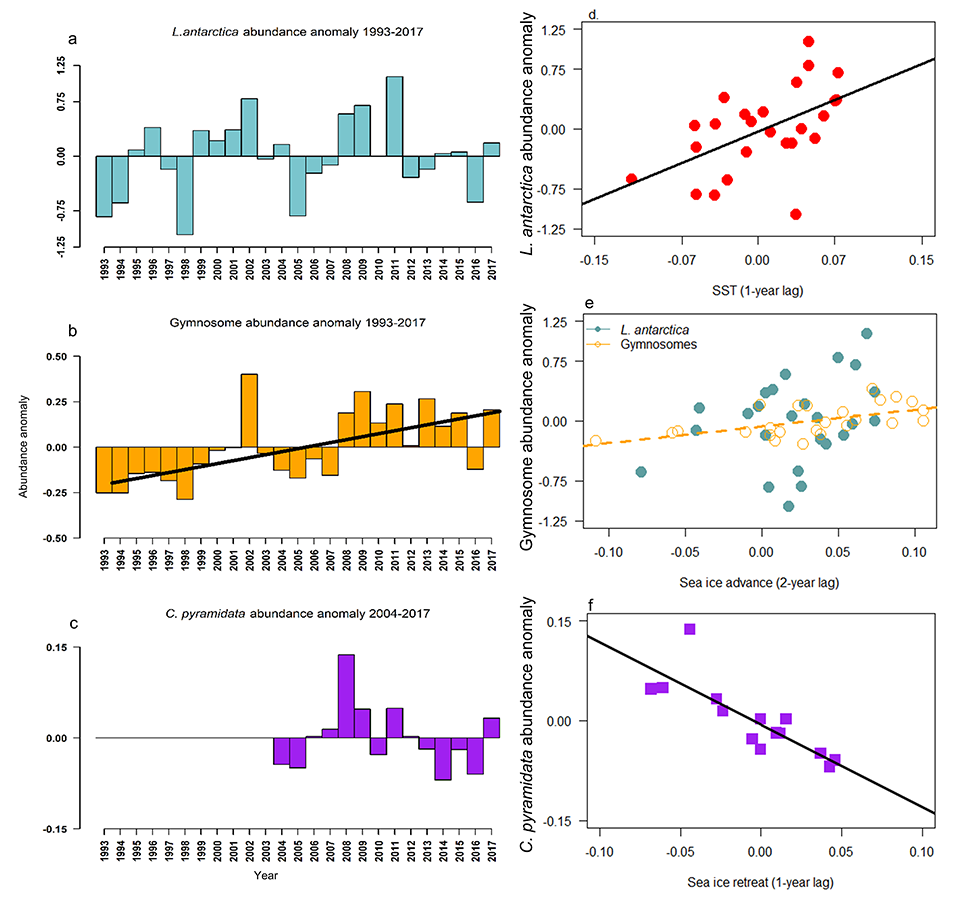
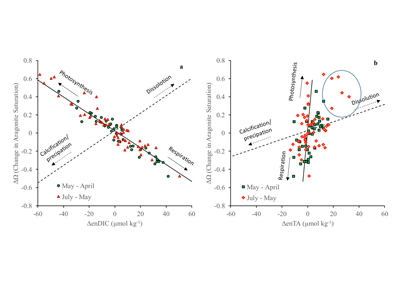
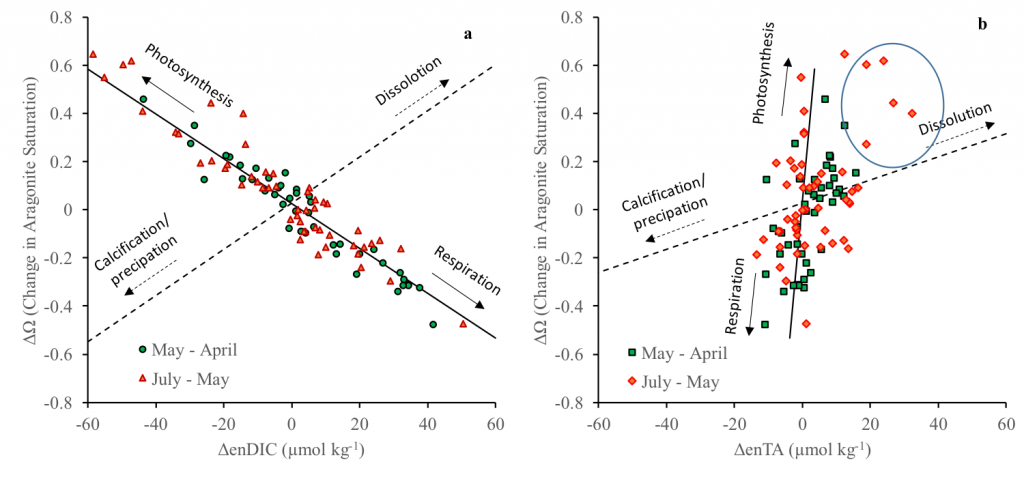
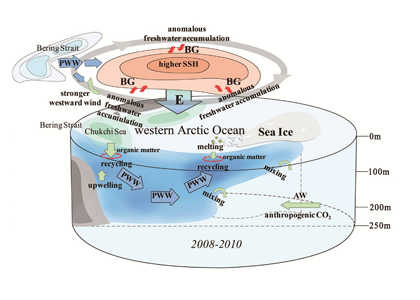
Sunrise and sunset are the main cues driving zooplankton diel vertical migration (DVM) throughout the world’s oceans. These marine animals balance the trade-off between feeding in surface waters at night and avoiding predation during the day at depth. Near-constant daylight during polar summer was assumed to dampen these daily migrations. In a recent paper published in Deep-Sea Research I, authors assessed austral summer DVM patterns for 15 taxa over a 9-year period. Despite up to 22 hours of sunlight, a diverse array of zooplankton – including copepods, krill, pteropods, and salps – continued DVM.
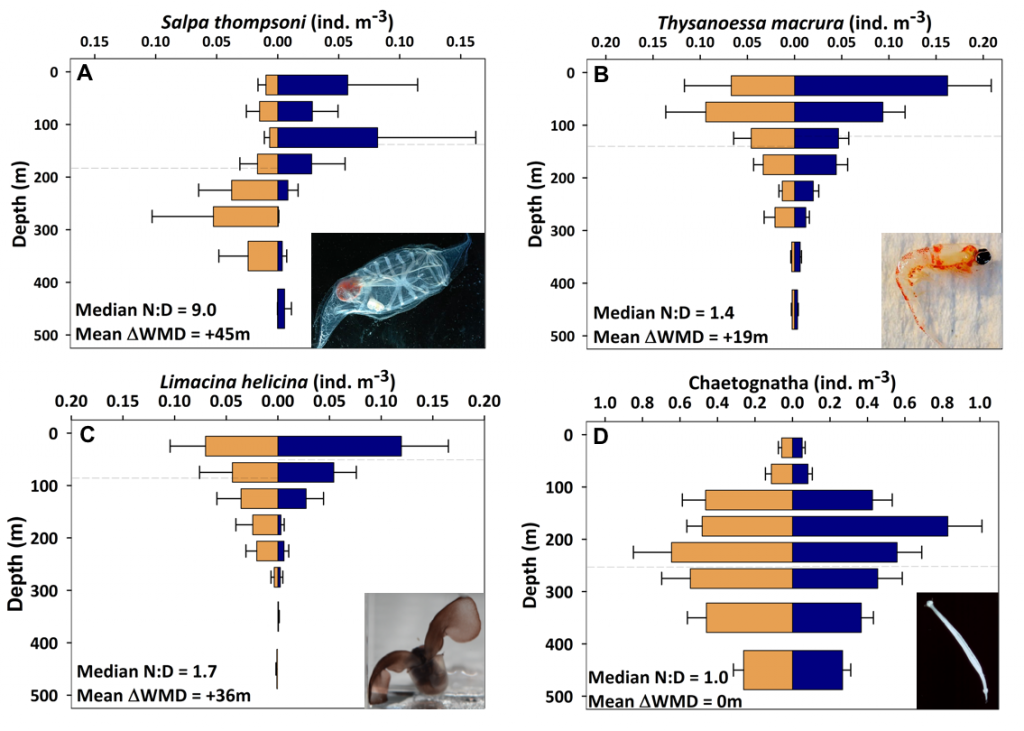
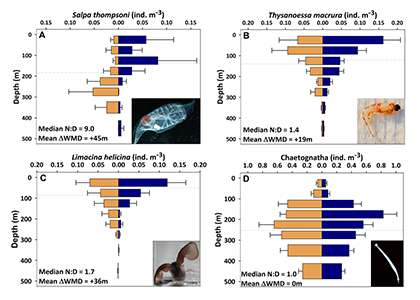
Figure caption: Mean day (orange) and night (blue) abundance of (A) the salp Salpa thompsoni, (B) the krill species Thysanoessa macrura, (C) the pteropod Limacina helicina, and (D) chaetognaths sampled at discrete depth intervals from 0-500m. Horizontal dashed lines indicate weighted mean depth (WMD). N:D is the night to day abundance ratio for 0-150 m. Error bars indicate one standard error. Sample size n = 12 to 22. Photos by Larry Madin, Miram Gleiber, and Kharis Schrage.
The Palmer Antarctica Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) Program conducted this study using a MOCNESS (Multiple Opening/Closing Net and Environmental Sensing System) to collect depth-stratified samples west of the Antarctic Peninsula. The depth range of migrations during austral summer varied across taxa and with daylength and phytoplankton biomass and distribution. While most taxa continued some form of DVM, others (e.g., carnivores and detritivores) remained most abundant in the mesopelagic zone, regardless of photoperiod, which likely impacted the attenuation of vertical carbon flux. Given the observed differences in vertical distribution and migration behavior across taxa, ongoing changes in Antarctic zooplankton assemblages will likely impact carbon export pathways. More regional, taxon-specific studies such as this are needed to inform efforts to model zooplankton contributions to the biological carbon pump.
Authors:
John Conroy (VIMS, William & Mary)
Deborah Steinberg (VIMS, William & Mary)
Patricia Thibodeau (VIMS, William & Mary; currently University of Rhode Island)
Oscar Schofield (Rutgers University)