Look no further. This primer article explains what an ocean biogeochemical model is, how such a model is designed and applied, and includes easily accessible code examples. Refresh your memory on commonly used metrics for model evaluation through model-data comparison. Get introduced to the underlying rationale, mechanics, applications, and pitfalls of data assimilation for parameter optimization, state estimation, and observing system design. Peruse overviews of available community code repositories and observational databases. And tour some of the important applications of ocean biogeochemical models for carbon accounting, ocean deoxygenation and acidification studies, and fisheries yield projections. The primer also includes recommendations for best practices in ocean biogeochemical modeling and discusses current limitations and anticipated future developments and challenges. First and foremost, the article is an invitation to get involved.
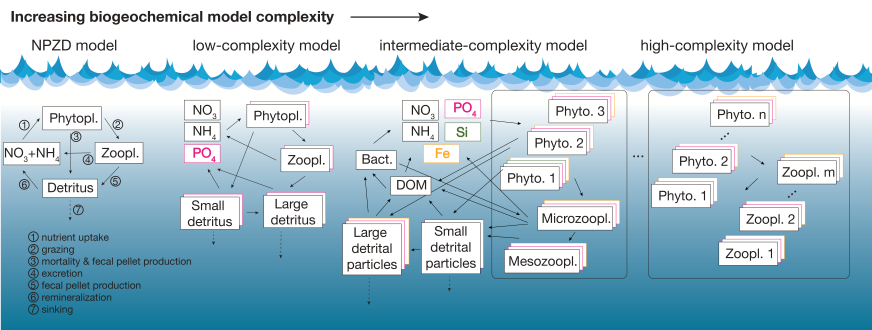
Figure caption: Schematic representation of the varying level of complexity in biogeochemical models. State variables are indicated by the boxes where different colors correspond to different elemental currencies. The black arrows indicate selected biogeochemical transformations. The simplest, the nutrient–phytoplankton– zooplankton–detritus (NPZD) model, includes four state variables and one nutrient currency, often nitrogen. A typical low-complexity model includes several nutrients and nutrient currencies. Chlorophyll is omitted in the schematic, although many models have a chlorophyll state variable for each phytoplankton group to account for photoacclimation.
Authors
Katja Fennel (Dalhousie University)
Jann Paul Mattern (University of California, Santa Cruz)
Scott C. Doney (University of Virginia)
Laurent Bopp (Institute Pierre Simon Laplace)
Andrew M. Moore (University of California, Santa Cruz)
Bin Wang (Dalhousie University)
Liuqian Yu (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology)
Twitter @katjafennel @ScottDoney1 @laurent_bopp @DalhousieU @uvaevsc